Left handed guitars are specifically designed for left-handed players, offering a comfortable and natural playing experience. At guitarplayers.net, we understand the importance of having the right instrument to match your playing style and physical needs. Discover the nuances of left-handed guitars, and unlock your full potential as a guitarist. We will explore the construction, setup, and benefits of using a left-handed guitar, empowering you to make an informed decision. Learn more about guitar playing techniques, musical instrument insights, and guitar accessories at guitarplayers.net.
1. What Truly Differentiates a Left Handed Guitar From a Right Handed One?
The construction and setup of the instruments are the most significant differences between right-handed and left-handed guitars. While it might seem simple to just flip a right-handed guitar and restring it, several crucial factors ensure a left-handed guitar provides optimal playability and sound quality. These factors include string length, string tension arrangement, frequency response, and ergonomics.
1.1. String Length and Intonation
String length, particularly its compensation, is crucial for accurate intonation. Intonation refers to how well a guitar stays in tune across the entire fretboard. Typically, bass strings (thicker strings) need to be longer than treble strings (thinner strings). This difference in length compensates for the varying tension and thickness of the strings.
Many acoustic guitars have bridges with fixed compensation angles. When a right-handed guitar is simply turned upside down and restrung for left-handed playing, it creates a compound error in string length compensation. As a result, the guitar will struggle to stay in tune across both the lower and upper registers.
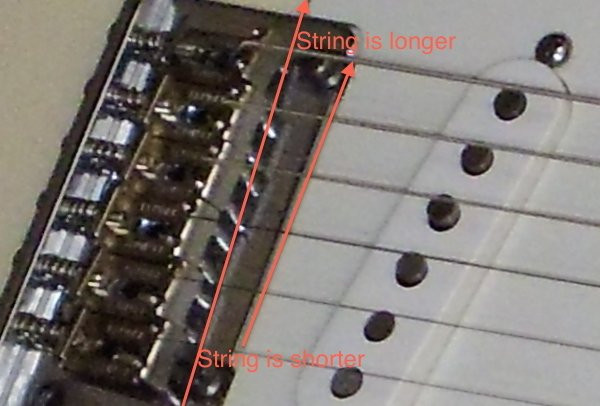 Acoustic guitar bridge with saddle compensation for intonation
Acoustic guitar bridge with saddle compensation for intonation
1.2. String Tension
Guitars are built to handle the specific tension differences between the bass and treble sides. Right-handed guitars are designed to have greater pounds per square inch on the bass side and lesser pounds per square inch on the treble side. This is particularly important for acoustic guitars because of their delicate body structure and how it vibrates. The bracing inside the guitar is designed to maximize the resonance based on these tension differences.
Turning a guitar upside down can create unwanted side effects because the tension is now reversed. For example, here is tension chart information from Curt Mangan strings.
click here for String Tension chart on their website
1.3. Frequency Response and Tone
The frequency response and tone of a guitar are significantly influenced by the tension arrangement of the strings and the resonant qualities of the instrument. The maker’s consistent efforts to construct instruments with a high-quality, pleasing tone involve careful consideration of every detail, from humidity to the type, weight, and form of the wood, glue, and hardware. Converting a right-handed guitar to a left-handed one by restringing it may compromise these carefully balanced elements, potentially leading to a less-than-ideal sound.
1.4. Ergonomics
The ergonomic design of a guitar ensures comfortable playability. When you play a guitar designed for the opposite hand, you essentially turn it upside down, which can render certain features useless. For instance, a cutaway body, designed to facilitate access to higher notes on the fretboard, loses its functionality. Electronic controls become difficult to reach, and hardware components may need alteration or replacement.
While some, like Jimi Hendrix, have made it work to their advantage, these adjustments can be time-consuming and expensive. Jimi Hendrix famously played right-handed guitars upside down and restrung. This gave him a unique sound and playing style, but it’s not the most practical solution for most guitarists.
2. Who Is a Left Handed Guitar Designed For?
A left handed guitar is primarily designed for left-handed individuals who find it more comfortable and natural to fret notes with their right hand and strum or pick with their left hand. While some left-handed individuals can learn to play a right-handed guitar, many find that using a left-handed guitar allows them to progress more quickly and play with greater ease.
2.1. Is a Left Handed Guitar Only For Left Handed People?
Yes, left-handed guitars are designed specifically for left-handed individuals. The design caters to the natural inclination of left-handed players, making the learning process more intuitive.
2.2. Why Is Playing a Left Handed Guitar More Comfortable For Left Handed Players?
Playing a left-handed guitar is more comfortable for left-handed players because it aligns with their natural dexterity and coordination. The dominant hand, which is typically the left hand for left-handed individuals, is used for strumming or picking, while the non-dominant hand is used for fretting notes. This setup allows for greater precision and control in both hands, leading to improved playing ability and reduced strain.
2.3. Can a Left Handed Person Learn on a Right Handed Guitar?
Yes, a left-handed person can learn to play a right-handed guitar, and some do so successfully. However, it often requires more effort and can feel less natural, especially in the beginning. Some left-handed players find that they can adapt to playing a right-handed guitar, but others may struggle with coordination and dexterity.
2.4. What Are the Advantages of Playing a Left Handed Guitar If You’re Left Handed?
The advantages of playing a left-handed guitar if you’re left-handed include:
- Increased Comfort: The guitar is designed to fit comfortably in your hands and body.
- Improved Dexterity: Your dominant hand can handle the more complex task of fretting.
- Natural Feel: The instrument aligns with your natural coordination.
- Faster Learning: Many left-handed players find they learn faster on a left-handed guitar.
2.5. Do I Need a Special Teacher To Learn Left Handed Guitar?
While not strictly necessary, a teacher experienced with left-handed guitar playing can be beneficial. They can offer specific guidance on technique and address any unique challenges you might face. However, any competent guitar teacher should be able to instruct a left-handed student. You can also find plenty of resources online, including lessons and tutorials, specifically for left-handed guitarists at guitarplayers.net.
3. What Are The Key Differences In Construction Of Left And Right Handed Guitars?
The key differences in the construction of left- and right-handed guitars lie in the mirror-image design of the instrument. This includes the nut, bridge, bracing (in acoustic models), and the placement of any controls or cutaways. These differences ensure that the guitar is ergonomically suited for left-handed players and that it functions correctly when strung for left-handed playing.
3.1. Nut and Bridge
The nut and bridge are designed to accommodate the strings correctly. On a left-handed guitar, the nut slots are cut in reverse order to match the string gauges, and the bridge saddle is often angled in the opposite direction to ensure proper intonation.
3.2. Bracing (Acoustic Guitars)
In acoustic guitars, the internal bracing pattern is often mirrored to provide optimal support and sound projection for left-handed playing. The bracing pattern is crucial for the structural integrity of the guitar and its tonal qualities.
3.3. Controls and Cutaways
If the guitar has electronic controls, such as volume and tone knobs, these are typically positioned to be easily accessible to a left-handed player. Similarly, any cutaways on the body are designed to facilitate access to the upper frets for left-handed players.
3.4. Headstock
While not always the case, some left-handed guitars feature a reversed headstock. This can alter the string tension and potentially affect the tone and feel of the guitar.
3.5. Pickguards
The pickguard on a left-handed guitar is placed to protect the body from scratches caused by a left-handed player’s strumming or picking.
4. What Types Of Guitars Are Available In Left Handed Versions?
Almost all types of guitars are available in left-handed versions, including acoustic guitars, electric guitars, bass guitars, and classical guitars. This ensures that left-handed players have access to the same wide range of instruments as right-handed players, allowing them to explore different genres and playing styles.
4.1. Acoustic Guitars
Left-handed acoustic guitars are available in various styles, including dreadnought, concert, and jumbo models. Brands like Taylor, Martin, and Yamaha offer left-handed versions of their popular acoustic guitars.
4.2. Electric Guitars
Left-handed electric guitars are widely available, with models ranging from classic designs like the Fender Stratocaster and Gibson Les Paul to more modern designs. Many major manufacturers, such as Fender, Gibson, Ibanez, and PRS, offer left-handed versions of their electric guitars.
4.3. Bass Guitars
Left-handed bass guitars are also available, allowing left-handed bassists to play comfortably. Fender, Sadowsky, and Ibanez produce left-handed versions of their bass guitars.
4.4. Classical Guitars
Left-handed classical guitars are less common but can still be found. These guitars are designed with the same specifications as right-handed classical guitars but with a mirrored design for left-handed players.
4.5. Other Instruments
Beyond the main categories, other instruments like banjos, mandolins, and ukuleles are sometimes available in left-handed versions, though they may be harder to find.
5. Where Can I Buy a Left Handed Guitar?
Left handed guitars can be purchased from various sources, including online retailers, local music stores, and directly from guitar manufacturers. When buying a left-handed guitar, consider factors such as the type of guitar, brand, price, and return policy.
5.1. Online Retailers
Online retailers like Sweetwater, Guitar Center, and Amazon offer a wide selection of left-handed guitars. Shopping online provides the convenience of browsing many models and reading customer reviews.
5.2. Local Music Stores
Local music stores often carry a selection of left-handed guitars. Buying from a local store allows you to try out the guitar before purchasing and receive personalized advice from knowledgeable staff.
5.3. Guitar Manufacturers
Some guitar manufacturers, such as Fender and Gibson, allow you to purchase directly from their website. This can be a good option if you are looking for a specific model or want to customize your guitar.
5.4. Used Guitars
Consider purchasing a used left-handed guitar to save money. Websites like Reverb and eBay are great places to find used guitars. Just be sure to inspect the guitar carefully before buying it.
5.5. Custom Shops
For a truly personalized instrument, consider having a left-handed guitar custom-built by a luthier or custom shop. This option allows you to specify every detail of the guitar, from the wood and hardware to the neck profile and finish.
6. What Are Some Famous Left Handed Guitar Players?
Several famous guitar players are left-handed, including Jimi Hendrix, Paul McCartney, Tony Iommi, Albert King, and Kurt Cobain. These musicians have made significant contributions to music and have inspired countless guitarists.
6.1. Jimi Hendrix
Jimi Hendrix, known for his innovative and virtuosic guitar playing, famously played a right-handed Fender Stratocaster upside down and restrung for left-handed playing.
6.2. Paul McCartney
Paul McCartney, the legendary bassist and vocalist for The Beatles, plays a left-handed Höfner bass guitar.
6.3. Tony Iommi
Tony Iommi, the guitarist for Black Sabbath, is a left-handed player who had to adapt his playing style after an accident that damaged his right hand.
6.4. Albert King
Albert King, a blues guitar icon, played a right-handed guitar upside down, without restringing it, creating a unique and distinctive sound.
6.5. Kurt Cobain
Kurt Cobain, the frontman and guitarist for Nirvana, played left-handed guitars, including Fender Mustangs and Jaguars.
7. Are Left Handed Guitars More Expensive?
Left handed guitars can sometimes be slightly more expensive than their right-handed counterparts due to lower production volumes and specialized manufacturing. However, the price difference is often minimal, and many manufacturers offer left-handed models at the same price as right-handed models.
7.1. Supply and Demand
The primary reason for the potential price difference is supply and demand. Because there are fewer left-handed players than right-handed players, manufacturers produce fewer left-handed guitars. This lower production volume can lead to higher prices.
7.2. Manufacturing Costs
Manufacturing left-handed guitars often requires additional setup and tooling, which can increase production costs. These costs may be passed on to the consumer in the form of slightly higher prices.
7.3. Retailer Markups
Some retailers may mark up the price of left-handed guitars due to their perceived rarity. However, it’s possible to find left-handed guitars at competitive prices by shopping around and comparing prices from different retailers.
7.4. Brands and Models
The price difference between left-handed and right-handed guitars can also depend on the brand and model. Some manufacturers offer left-handed versions of their guitars at the same price as right-handed versions, while others may charge a premium.
7.5. Finding Affordable Options
Despite the potential for higher prices, many affordable left-handed guitars are available. Consider looking for used guitars or shopping during sales and promotions to save money.
8. Can I Convert A Right Handed Guitar To Left Handed?
Converting a right-handed guitar to a left-handed guitar is possible, but it is not always recommended. Simple restringing can lead to intonation and ergonomic issues.
8.1. Restringing
The most straightforward method is to restring the guitar for left-handed playing. However, this can cause intonation problems because the nut and saddle are designed for right-handed playing.
8.2. Replacing the Nut and Saddle
To improve intonation, you can replace the nut and saddle with left-handed versions. This involves removing the existing nut and saddle and installing new ones that are properly slotted and compensated for left-handed playing.
8.3. Bridge Adjustment
On some guitars, the bridge may need to be adjusted or replaced to achieve proper intonation. This is more common on acoustic guitars with fixed bridges.
8.4. Control Placement
If the guitar has electronic controls, you may need to relocate them to be more accessible for left-handed playing. This can involve drilling new holes and rewiring the controls.
8.5. Professional Setup
It is recommended to have a professional guitar technician perform the conversion to ensure that the guitar is properly set up and intonated for left-handed playing.
9. What Accessories Do I Need For A Left Handed Guitar?
The accessories needed for a left-handed guitar are generally the same as those needed for a right-handed guitar, including picks, a strap, a tuner, a case, and a cable (for electric guitars). However, some accessories, like straps and guitar stands, may be designed with left-handed players in mind.
9.1. Picks
Picks are an essential accessory for any guitar player. Choose picks that feel comfortable in your hand and produce the desired tone.
9.2. Strap
A guitar strap is necessary for playing while standing. Look for a strap that is adjustable and comfortable to wear. Some straps are designed with left-handed players in mind, with the strap button positioned for optimal balance.
9.3. Tuner
A tuner is crucial for keeping your guitar in tune. Electronic tuners are easy to use and provide accurate tuning.
9.4. Case
A guitar case is essential for protecting your guitar during transport and storage. Choose a hard case for maximum protection or a soft case for lighter travel.
9.5. Cable (For Electric Guitars)
If you are playing an electric guitar, you will need a cable to connect it to an amplifier. Look for a high-quality cable that will provide a clear and reliable signal.
9.6. Guitar Stand
A guitar stand is a convenient way to store your guitar when you are not playing it. This helps protect the guitar from damage and keeps it readily accessible.
10. How Do I Care For A Left Handed Guitar?
Caring for a left-handed guitar is similar to caring for a right-handed guitar, involving regular cleaning, proper storage, and periodic maintenance. Regular care will help keep your guitar in good condition and ensure that it plays well for years to come.
10.1. Cleaning
Clean your guitar regularly with a soft, dry cloth to remove dust, fingerprints, and smudges. For stubborn dirt, use a guitar polish specifically designed for the finish on your guitar.
10.2. Storage
Store your guitar in a case or on a stand in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. This will help prevent damage to the wood and finish.
10.3. String Changes
Change your strings regularly to maintain optimal tone and playability. The frequency of string changes depends on how often you play and the type of strings you use.
10.4. Humidity Control
Maintain proper humidity levels to prevent the wood from drying out or warping. Use a humidifier or dehumidifier as needed to keep the humidity level between 40% and 60%.
10.5. Professional Setup
Have your guitar professionally set up periodically to ensure that it is playing at its best. A setup includes adjusting the action, intonation, and neck relief.
FAQ About Left Handed Guitars
1. Is it harder to find left-handed guitars?
Yes, left-handed guitars can be less common than right-handed models, but most major brands offer a selection of left-handed options.
2. Can I play a right-handed guitar upside down if I’m left-handed?
While possible, it’s not ideal due to intonation and ergonomic issues. It’s better to get a guitar designed for left-handed players.
3. Do left-handed guitars sound different from right-handed guitars?
No, the sound quality is the same. The only difference is the mirrored construction to suit left-handed players.
4. Are left-handed guitar lessons different from right-handed lessons?
The fundamentals are the same, but a left-handed teacher may provide specific tips and techniques tailored to left-handed players.
5. Can I restring a right-handed guitar for left-handed playing?
Yes, but it’s not recommended without adjusting the nut and saddle for proper intonation.
6. Are there famous left-handed guitar players?
Yes, Jimi Hendrix, Paul McCartney, and Kurt Cobain are some well-known left-handed guitarists.
7. Is a left-handed guitar more expensive than a right-handed one?
Sometimes, but prices are becoming more competitive as demand increases.
8. What is the best way to learn left-handed guitar?
Find a qualified teacher or use online resources designed for left-handed players.
9. What are the essential accessories for a left-handed guitar?
Picks, straps, tuners, cases, and cables are essential for all guitarists, including left-handed players.
10. Can I convert my right-handed guitar to a left-handed guitar?
Yes, but it’s best to have a professional do it to ensure proper setup and intonation.
Ready to explore the world of left-handed guitars? Discover a wealth of resources, lessons, and a vibrant community at guitarplayers.net. Whether you’re seeking expert advice, in-depth reviews, or a place to connect with fellow guitar enthusiasts, guitarplayers.net is your ultimate destination. Don’t miss out—visit guitarplayers.net today and start your musical journey off on the right foot (or left hand)! For personalized assistance, contact us at 1140 Boylston Street, Boston, MA 02215, United States. Call +1 (617) 747-2261 or visit our website at guitarplayers.net.