Remembering chords on the guitar can be a challenge, but it’s definitely achievable with the right strategies, and at guitarplayers.net, we’re dedicated to helping guitarists of all levels master this skill. We’ll explore proven techniques to enhance your chord memorization, turning daunting finger positions into confident, musical expression with chord charts, chord diagrams, and memory aids.
1. Understanding the Science of Memorizing Guitar Chords
To effectively memorize guitar chords, it helps to understand the underlying principles of memory and how they apply to learning music.
Repetition is the cornerstone of memory. Research indicates that it typically takes around 20 repetitions of a task for the brain to start encoding it into memory. This insight, highlighted by studies at music institutions, suggests that consistent, focused practice is essential for chord memorization. Instead of just repeating something 5-10 times, keep practicing to improve your skills.
1.1 Why Repetition Matters in Chord Learning
Repetition solidifies neural pathways, making recall easier over time. Engaging in consistent practice, repeating chord transitions and progressions 20-50 times over several days, significantly improves both skill and memory.
1.2 How Sensory Engagement Enhances Memory
Our senses play a crucial role in memory formation. Engaging multiple senses during practice creates stronger, more vivid memories. As Berklee College of Music pointed out in a 2023 study, actively listening to the sound of each chord, feeling the strings under your fingers, and visually noting the finger patterns on the fretboard enhances memorization.
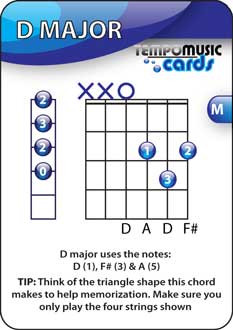 D major chord diagram for guitar
D major chord diagram for guitar
Alternative Text: The D major chord card shows finger position, guitar tab, and the notes in the chord.
2. Practical Tips for Effective Chord Memorization
These practical tips will help you create a solid foundation for memorizing guitar chords, combining repetition, sensory engagement, and mnemonic devices.
2.1 Tip #1: Repeat Everything at Least 20 Times
Committing to a minimum of 20 repetitions before moving on to new material ensures that the brain begins the memorization process, solidifying the neural pathways associated with each chord.
2.2 Tip #2: Engage Multiple Senses
Involving your senses enhances memory retention. Pay close attention to the sound, feel, and visual aspects of playing each chord to strengthen the connection between your senses and memory.
2.3 Tip #3: Use Mnemonic Devices
Mnemonics are memory aids that can help you remember chord shapes and finger placements. Creating associations or acronyms can make the chords easier to recall.
3. A Step-by-Step Method to Memorize Guitar Chords
Follow these steps to memorize guitar chords in an easy way.
3.1 Step 1: Choose Four Chords to Memorize
Selecting a small set of chords to focus on prevents overwhelm and allows for deeper learning. Using tools like flashcards can introduce variety and challenge you to learn chords outside your comfort zone.
3.2 Step 2: Study the Chords
Take the time to understand each chord’s structure, including the notes it contains, the intervals between them, and the finger positions required to play it. This deeper understanding creates a more robust memory trace.
- The chord uses only four strings – D, G, B, E
- The notes used are D, F#, A
- The chord is a Major chord
- Only the first three fingers are used
- The finger pattern creates a triangle shape on the fretboard
- The Guitar TAB layout for the chord (shown on the left of the card) creates a pattern 0 2 3 2
- The lowest note is the low D string
3.3 Step 3: Visualize Playing the Chords
Visualization is a powerful tool for reinforcing memory. Mentally rehearse the finger placements and transitions between chords to prime your brain for physical performance.
3.4 Step 4: Play the Progression 20+ Times
Consistent repetition is key to solidifying muscle memory. Play the chord progression slowly and deliberately, focusing on accuracy and smooth transitions.
3.5 Step 5: Take a Break
Brief breaks allow your brain to consolidate the information you’ve learned. Stepping away from the guitar for a few minutes can improve retention and prevent mental fatigue.
3.6 Step 6: Repeat
Regular practice is essential for long-term retention. Review the chords and progressions you’ve learned each day to reinforce your memory and build confidence.
4. Mastering Chord Progressions for Enhanced Memorization
Understanding chord progressions is essential for memorizing chords effectively.
4.1 Common Chord Progressions
Familiarize yourself with common chord progressions like I-IV-V-I (e.g., G-C-D-G) to understand how chords relate to each other within a key. Recognizing these patterns will make it easier to anticipate and remember chord changes.
4.2 Practicing Progressions
Practice chord progressions in different keys and tempos to develop versatility and muscle memory. Use a metronome to maintain a steady beat and focus on smooth transitions between chords.
4.3 Analyzing Songs
Analyze songs you enjoy playing to identify the chord progressions they use. Understanding the underlying structure of songs will deepen your understanding of harmony and make it easier to memorize chords and songs.
5. Utilizing Technology for Chord Memorization
Take advantage of technology to enhance your chord memorization efforts.
5.1 Guitar Chord Apps
Explore guitar chord apps that offer chord diagrams, audio samples, and interactive exercises to help you learn and memorize chords.
5.2 Online Resources
Utilize online resources like guitarplayers.net, which offer chord charts, tutorials, and community forums where you can ask questions and share tips with other guitarists.
5.3 Recording and Playback
Record yourself playing chord progressions and songs, and then listen back to identify areas for improvement. This feedback can help you refine your technique and reinforce your memory of chord changes.
6. Optimizing Your Practice Environment
Creating the right practice environment can significantly impact your ability to memorize guitar chords.
6.1 Minimize Distractions
Choose a quiet and comfortable space where you can focus without interruptions. Turn off your phone, close unnecessary tabs on your computer, and let your family or roommates know you need some uninterrupted practice time.
6.2 Set Realistic Goals
Break down your practice sessions into manageable chunks with specific goals. Instead of trying to learn too many chords at once, focus on mastering a few chords or a single chord progression during each session.
6.3 Stay Organized
Keep your guitar, chord charts, and other practice materials organized and easily accessible. This will help you stay focused and motivated during your practice sessions.
7. Advanced Techniques for Chord Memorization
Once you’ve mastered the basics, explore these advanced techniques to further enhance your chord memorization skills.
7.1 Chord Voicings
Experiment with different voicings of the same chord to add variety and depth to your playing. Learning multiple voicings of each chord will also improve your understanding of harmony and chord relationships.
7.2 Chord Inversions
Explore chord inversions, which involve changing the order of the notes in a chord while still maintaining its basic harmonic function. Understanding inversions will give you more flexibility in your playing and make it easier to create smooth transitions between chords.
7.3 Chord Substitutions
Learn about chord substitutions, which involve replacing one chord in a progression with another chord that has a similar harmonic function. Experimenting with chord substitutions can add color and interest to your playing and help you develop a deeper understanding of harmony.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Memorizing Chords
Be aware of these common pitfalls that can hinder your chord memorization efforts.
8.1 Rushing the Process
Avoid trying to learn too many chords too quickly. Take your time to understand each chord thoroughly and practice it consistently before moving on to the next one.
8.2 Neglecting Fundamentals
Don’t skip over the fundamentals of guitar playing, such as proper finger placement, posture, and technique. A solid foundation will make it easier to learn and memorize chords.
8.3 Ignoring Ear Training
Develop your ear training skills to recognize chords and chord progressions by ear. This will not only improve your ability to memorize chords but also enhance your overall musicianship.
9. The Role of Active Recall in Chord Memorization
Active recall is a powerful technique for reinforcing memory and improving retention.
9.1 Testing Yourself
Regularly test yourself on the chords you’ve learned by trying to play them from memory without looking at chord charts or diagrams.
9.2 Spaced Repetition
Use spaced repetition techniques to review chords at increasing intervals over time. This will help you transfer the information from short-term to long-term memory.
9.3 Teaching Others
Teach the chords you’ve learned to others. Explaining the concepts to someone else will solidify your understanding and improve your ability to recall the information.
10. Maintaining Long-Term Chord Memory
Consistency is key to maintaining long-term chord memory.
10.1 Regular Practice
Continue to practice the chords you’ve learned on a regular basis to reinforce your memory and prevent forgetting.
10.2 Review and Refresh
Periodically review the chords you’ve learned to refresh your memory and identify any areas where you may need to brush up.
10.3 Apply Your Knowledge
Apply your knowledge of chords by playing songs, improvising, and composing your own music. This will not only reinforce your memory but also make learning chords more enjoyable and rewarding.
11. How to Memorize Barre Chords
Barre chords can be particularly challenging to memorize due to the finger strength and precision required. Here’s how to tackle them:
11.1 Mastering the Barre Technique
Ensure your barre is clean and consistent. Practice pressing down firmly behind the fret with your index finger to get a clear sound from all strings.
11.2 Visualizing the Shape
Understand the root note and shape of the barre chord. For example, knowing the E shape and A shape barre chords allows you to play major and minor variations up and down the neck.
11.3 Practicing Transitions
Work on smooth transitions between barre chords and open chords. Start slowly and gradually increase your speed as your finger strength and accuracy improve.
12. The Importance of Understanding Music Theory
A basic understanding of music theory can greatly aid chord memorization and application.
12.1 Chord Construction
Learn how chords are constructed from scales and intervals. Understanding the relationships between notes in a chord will make it easier to remember finger placements.
12.2 Key Signatures
Familiarize yourself with key signatures and the chords that naturally occur in each key. This knowledge will help you anticipate chord changes and understand chord progressions.
12.3 Roman Numeral Analysis
Use Roman numeral analysis to identify the function of each chord in a progression. This will give you a deeper understanding of harmony and make it easier to memorize chord progressions.
13. Memorizing Chords in Different Genres
Different genres of music often feature distinct chord progressions and voicings.
13.1 Blues
Focus on learning common blues chords like dominant 7th chords and minor pentatonic scales.
13.2 Rock
Master power chords and common rock progressions like I-V-vi-IV.
13.3 Jazz
Explore jazz chords like major 7th, minor 7th, and dominant 7th chords, as well as chord substitutions and alterations.
14. Developing Your Musical Ear for Chord Recognition
Ear training is a valuable skill that can greatly enhance your ability to memorize and recognize chords.
14.1 Interval Training
Practice identifying intervals by ear. This will help you recognize the relationships between notes in a chord.
14.2 Chord Identification
Use ear training exercises to identify chords by ear. Start with simple major and minor chords, and then gradually progress to more complex chords.
14.3 Song Transcribing
Try transcribing songs by ear. This will not only improve your ear training skills but also deepen your understanding of harmony and chord progressions.
15. Creating Your Own Chord Charts and Diagrams
Creating your own chord charts and diagrams can be a helpful way to reinforce your memory of chord shapes.
15.1 Hand-Drawn Charts
Draw your own chord charts and diagrams, labeling each finger position and note.
15.2 Digital Charts
Use digital tools like guitar chord software or online chart generators to create professional-looking chord charts.
15.3 Personalized Notation
Develop your own notation system for chords, such as using colors or symbols to represent different finger positions.
16. Connecting Chords to Songs You Love
One of the most effective ways to memorize chords is to connect them to songs you enjoy playing.
16.1 Learning Songs
Choose songs that feature the chords you want to learn and practice playing them until you can play them from memory.
16.2 Song Analysis
Analyze the chord progressions and song structures of your favorite songs to deepen your understanding of harmony and chord relationships.
16.3 Performing
Perform the songs you’ve learned for others. This will not only reinforce your memory but also give you a sense of accomplishment and motivation to continue learning.
17. The Power of Group Learning and Community
Learning in a group or community setting can provide support, motivation, and valuable insights.
17.1 Guitar Lessons
Take guitar lessons from a qualified instructor who can provide personalized guidance and feedback.
17.2 Group Classes
Attend group guitar classes where you can learn from other students and share your experiences.
17.3 Online Forums
Participate in online guitar forums and communities where you can ask questions, share tips, and connect with other guitarists.
18. Using Flashcards for Chord Memorization
Flashcards are a versatile tool for memorizing guitar chords.
18.1 Chord Diagrams
Create flashcards with chord diagrams on one side and the chord name on the other.
18.2 Chord Voicings
Include multiple voicings of each chord on separate flashcards.
18.3 Chord Progressions
Create flashcards with chord progressions on one side and the Roman numeral analysis on the other.
19. Incorporating Movement and Muscle Memory
Movement and muscle memory can play a significant role in chord memorization.
19.1 Finger Exercises
Practice finger exercises to improve your dexterity and coordination.
19.2 Scale Practice
Practice scales to develop finger strength and muscle memory.
19.3 Blindfolded Practice
Try practicing chords blindfolded to rely on muscle memory and tactile feedback.
20. The Benefits of Regular Performance
Performing regularly can provide motivation, boost confidence, and reinforce your memory of chords and songs.
20.1 Open Mic Nights
Participate in open mic nights and perform for a live audience.
20.2 Jam Sessions
Attend jam sessions and improvise with other musicians.
20.3 Recording Yourself
Record yourself playing and share your music online.
Remembering chords on the guitar requires dedication, patience, and the right strategies. By understanding the science of memory, utilizing practical tips, and incorporating advanced techniques, you can enhance your chord memorization skills and unlock your full potential as a guitarist. Remember to create a supportive practice environment, avoid common mistakes, and leverage the power of active recall and community learning.
Ready to take your guitar playing to the next level? Visit guitarplayers.net for a wealth of resources, including free lessons, chord charts, song tutorials, and a vibrant community of fellow guitar enthusiasts. Whether you’re a beginner just starting out or an experienced player looking to expand your skills, guitarplayers.net has everything you need to succeed. Join us today and start your journey to guitar mastery.
FAQ: How to Remember Chords on Guitar
1. What is the best way to memorize guitar chords quickly?
The most effective method involves studying chord diagrams, visualizing finger placements, and practicing chord transitions repeatedly. Consistent practice and engaging multiple senses enhance memory retention.
2. How many repetitions does it take to memorize a guitar chord?
Research suggests that it typically takes around 20 repetitions of a task for the brain to begin encoding it into memory. Consistent repetition is key to solidifying muscle memory.
3. Should I memorize chord diagrams or finger positions?
Focus on memorizing both chord diagrams and finger positions. Understanding the visual representation of the chord and the physical placement of your fingers will create a stronger memory trace.
4. How can I improve my chord transitions?
Practice smooth transitions between chords by focusing on economy of motion and using guide fingers. Start slowly and gradually increase your speed as your accuracy improves.
5. What are some common chord progressions to memorize?
Common chord progressions include I-IV-V-I, I-V-vi-IV, and ii-V-I. Familiarizing yourself with these progressions will help you understand how chords relate to each other within a key.
6. How can I use mnemonic devices to memorize chords?
Create associations or acronyms to help you remember chord shapes and finger placements. For example, you could use a mnemonic to remember the order of fingers on a chord.
7. What role does ear training play in chord memorization?
Ear training can help you recognize chords and chord progressions by ear, which can reinforce your memory and improve your overall musicianship.
8. How important is it to understand music theory for chord memorization?
A basic understanding of music theory can greatly aid chord memorization and application. Learning how chords are constructed from scales and intervals will make it easier to remember finger placements.
9. How can I stay motivated to practice chord memorization?
Set realistic goals, choose songs you enjoy playing, and join a guitar community or take lessons. Regular practice and a supportive environment will help you stay motivated.
10. Where can I find reliable resources for learning guitar chords?
Visit guitarplayers.net for a wealth of resources, including free lessons, chord charts, song tutorials, and a vibrant community of fellow guitar enthusiasts.
Address: 1140 Boylston Street, Boston, MA 02215, United States.
Phone: +1 (617) 747-2261.
Website: guitarplayers.net.
