Finding out what guitar you have involves identifying its brand, model, and unique features; Guitarplayers.net helps guitar enthusiasts like you quickly uncover the story behind your instrument, assess its worth, and connect with a community of fellow players. Whether you’re looking to identify vintage guitars, acoustic guitars, or electric guitars, understanding the instrument’s history enhances your appreciation for music and musicianship.
Table of Contents
- Why Is It Important To Identify Your Guitar?
- Step 1: Identifying The Guitar Brand
- Step 2: Locating The Serial Number On Your Guitar
- Step 3: Decoding The Serial Number
- Step 4: Examining Physical Features Of The Guitar
- Step 5: Checking The Guitar’s Hardware And Electronics
- Step 6: Researching The Guitar’s History
- Step 7: Consulting Experts And Online Communities
- Step 8: Using Online Guitar Identification Tools
- Step 9: Understanding The Impact Of Modifications On Value
- Step 10: Documenting Your Findings
- How To Use Guitar Brand-Specific Resources?
- How To Determine Guitar Value?
- How To Care For And Maintain Your Guitar After Identifying It?
- What Are The Common Mistakes To Avoid When Identifying A Guitar?
- What Are Some Famous Guitar Brands And Their Identifying Characteristics?
- How Does Guitarplayers.Net Help In Identifying And Learning About Guitars?
- What Are The Different Types Of Guitar Construction?
- What Are The Most Common Types Of Wood Used In Guitars?
- What Are The Key Differences Between Acoustic, Electric, And Bass Guitars?
- What Are Some Notable Guitar Innovations And Their Impact?
- How To Identify Counterfeit Guitars?
- What To Do With The Guitar Information You Have Found?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why Is It Important To Identify Your Guitar?
Identifying your guitar is important for several reasons:
- Determining Value: Knowing the make, model, and year of your guitar significantly impacts its market value.
- Historical Significance: Identifying a vintage guitar can reveal its history, connecting you to a legacy of music and craftsmanship.
- Maintenance and Repair: Accurate identification ensures you use the correct parts and methods for maintenance and repairs.
- Personal Connection: Understanding your guitar’s origins deepens your appreciation for the instrument.
Identifying your guitar not only enhances your connection to the instrument but also ensures you have the knowledge to properly care for it.
2. Step 1: Identifying The Guitar Brand
The first step in identifying your guitar is to determine its brand, which is often the easiest and most straightforward clue. The brand name is typically found on the headstock of the guitar. For acoustic guitars, you might also find a label inside the soundhole that includes the brand name, model name, and serial number.
Where to Look for the Brand Name:
- Headstock: The most common location for the brand name. Look for a logo or nameplate.
- Soundhole (Acoustic Guitars): Check for a label inside the soundhole, which often includes the brand and model information.
- Neck Plate (Electric Guitars): Some electric guitars, particularly Fenders, have the brand name on the neck plate.
Once you have identified the brand, you can start to narrow down the specific model and year of your guitar. This information is crucial for further research and valuation.
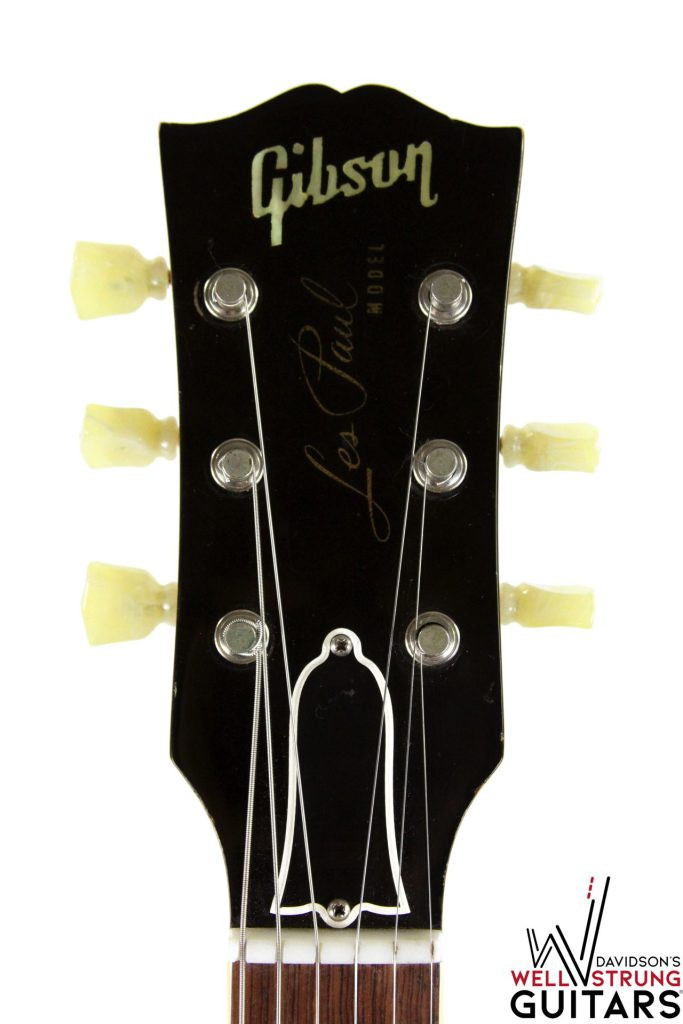 Guitar headstock featuring the brand logo, a key identifier in determining the guitar's origin
Guitar headstock featuring the brand logo, a key identifier in determining the guitar's origin
3. Step 2: Locating The Serial Number On Your Guitar
The serial number is a unique identifier assigned to your guitar by the manufacturer. It is essential for determining the exact year and model of your instrument. The location of the serial number varies depending on the brand and type of guitar.
Common Locations for Serial Numbers:
| Brand | Location |
|---|---|
| Gibson | Back of the headstock (solid-body), label inside the F-hole (hollow-body), inside the soundhole (acoustic) |
| Fender | Neck plate (1954 and newer), bridge plate (1950-1954), front or back of the headstock (modern models) |
| Gretsch | Hand-scribed on the back control covers or inside the control cavity, sometimes on the headstock |
| Rickenbacker | Stamped on the jack plate or the top of the headstock |
| Martin | Inside label or neck block |
Serial numbers can provide valuable information about when and where your guitar was made.
 Acoustic guitar label displaying the serial number, crucial for identifying the guitar's manufacturing details
Acoustic guitar label displaying the serial number, crucial for identifying the guitar's manufacturing details
4. Step 3: Decoding The Serial Number
Once you have located the serial number, the next step is to decode it. Different manufacturers use different serial number formats, so understanding the specific system used by your guitar’s brand is essential. Many brands have publicly available serial number guides that can help you determine the year of manufacture.
Resources for Decoding Serial Numbers:
- Fender Serial Number Guide: Provides information on dating Fender guitars based on their serial numbers.
- Gibson Serial Number Guide: Helps you determine the year of your Gibson guitar.
- Gruhn’s Guitar Guide: A comprehensive resource with serial number information for various vintage instruments.
If you cannot find a publicly listed serial number guide for your brand, consulting with experts or using online guitar identification tools can be helpful.
5. Step 4: Examining Physical Features Of The Guitar
Beyond the brand and serial number, examining the physical features of your guitar can provide additional clues about its identity. Details such as the body shape, finish, headstock design, and hardware can help narrow down the model and year.
Key Physical Features to Consider:
- Body Shape: Different guitar models have distinct body shapes. For example, a Fender Stratocaster has a different body shape than a Telecaster.
- Finish: The color and type of finish can indicate the guitar’s age and model.
- Headstock Design: The shape and design of the headstock can be unique to certain brands and models.
- Hardware: The type of pickups, bridge, and tuners can also help identify the guitar.
By carefully examining these physical features, you can gather valuable information that will aid in your identification process.
6. Step 5: Checking The Guitar’s Hardware And Electronics
The hardware and electronics of a guitar can provide valuable clues about its origin and authenticity. Checking the potentiometers (volume and tone controls) and other electronic components can reveal manufacturing dates that help narrow down the year of production.
How to Check Hardware and Electronics:
- Potentiometers: Look for codes printed or stamped on the underside or side of the potentiometers. The first three digits typically indicate the manufacturer code (e.g., “304” for Stackpole, “137” for CTS). The following digits represent the year and week of manufacture. For example, a code like “1376547” means the part was made by CTS in the 47th week of 1965.
- Pickups: Examine the pickups for any markings or codes that indicate the manufacturer and date of production.
- Wiring: Inspect the wiring for any unique characteristics that might indicate the guitar’s origin.
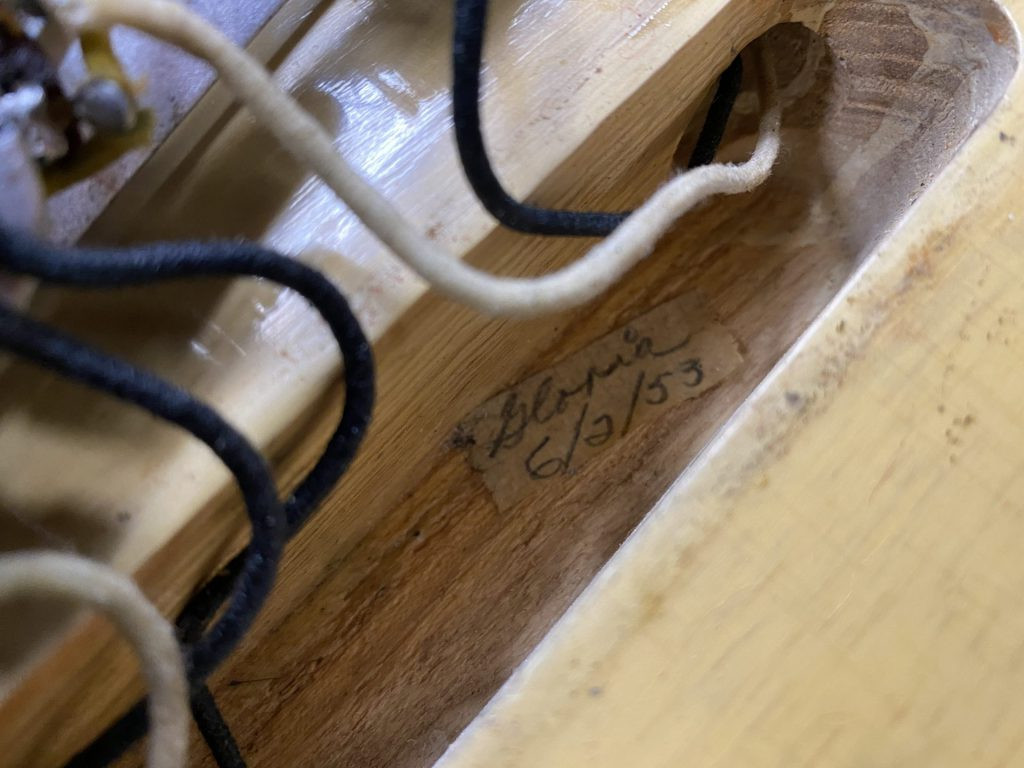 Close-up of guitar electronics showing date codes, which can help determine the guitar's production timeline
Close-up of guitar electronics showing date codes, which can help determine the guitar's production timeline
7. Step 6: Researching The Guitar’s History
Once you have gathered as much information as possible from the guitar itself, it’s time to delve into research. Online resources, guitar forums, and vintage guitar databases can provide a wealth of information about different models and their production years.
Online Resources for Guitar Research:
- Guitar Forums: Websites like the Fender Forum and Gibson Forum have knowledgeable communities that can help you identify your guitar.
- Vintage Guitar Databases: Websites like Vintage Guitar Magazine offer databases and articles that can assist in your research.
- Manufacturer Websites: Check the official websites of guitar manufacturers for historical information and model archives.
By researching the history of your guitar, you can piece together its story and gain a deeper understanding of its origins.
8. Step 7: Consulting Experts And Online Communities
When you’re stumped, consulting experts and online communities can be a game-changer. Experts often have years of experience and can identify subtle features that you might miss. Online communities provide a collective knowledge base where fellow guitar enthusiasts can offer insights and suggestions.
How to Engage Experts and Communities:
- Local Guitar Shops: Visit local guitar shops and ask for their opinion. Many shops have staff with expertise in vintage and rare guitars.
- Online Forums: Post photos and descriptions of your guitar on guitar forums. Be prepared to answer questions about its features and history.
- Appraisers: Consider hiring a professional appraiser who specializes in vintage guitars. They can provide a detailed assessment and valuation.
By tapping into the knowledge of experts and communities, you can often find the information you need to identify your guitar accurately. Guitarplayers.net is a great community for enthusiasts!
9. Step 8: Using Online Guitar Identification Tools
Several online tools can help you identify your guitar by analyzing its features and comparing them to databases of known models. These tools often use image recognition and other advanced technologies to assist in the identification process.
Popular Online Guitar Identification Tools:
- Guitar Dater Project: A website that allows you to input the serial number and other information to identify your guitar.
- Vintage Guitar Info: A comprehensive resource with information on various vintage guitars.
- Online Guitar Forums: Many forums have sections dedicated to guitar identification.
These tools can provide valuable insights and help you narrow down the possibilities.
10. Step 9: Understanding The Impact Of Modifications On Value
Modifications can significantly impact the value of a vintage guitar. Original, unmodified guitars are generally more valuable than those with replacement parts or alterations. Understanding the extent and nature of any modifications is crucial for accurately assessing your guitar’s value.
Common Modifications That Affect Value:
- Replacement Pickups: Swapping out the original pickups can decrease the guitar’s value, especially if the replacements are not period-correct.
- Refinishing: A refinished guitar is typically worth less than one with its original finish.
- Hardware Changes: Replacing original hardware like tuners, bridges, or knobs can lower the value.
- Structural Repairs: Significant repairs, such as neck resets or body cracks, can also affect the guitar’s value.
When evaluating your guitar, carefully document any modifications and consider how they might impact its worth.
11. Step 10: Documenting Your Findings
Throughout the identification process, it’s essential to keep detailed records of your findings. Documenting the brand, model, serial number, physical features, and any other relevant information will not only help you keep track of your progress but also provide valuable documentation for future appraisals or sales.
What to Include in Your Documentation:
- Photos: Take clear photos of the guitar from various angles, including close-ups of the headstock, body, and any unique features.
- Serial Number: Record the serial number and its location on the guitar.
- Physical Features: Describe the body shape, finish, hardware, and any other distinguishing characteristics.
- Research Notes: Keep notes on your research, including websites visited, forum discussions, and expert opinions.
By documenting your findings, you’ll create a comprehensive record that can be invaluable for understanding and preserving your guitar’s history.
12. How To Use Guitar Brand-Specific Resources?
Guitar brand-specific resources can be incredibly valuable when identifying your instrument. These resources often include detailed serial number guides, historical model information, and specifications that can help you pinpoint the exact year and model of your guitar.
Examples of Brand-Specific Resources:
- Fender: The Fender website offers a serial number lookup tool and historical information on their models.
- Gibson: Gibson provides serial number guides and detailed specifications for vintage and modern guitars.
- Martin: Martin offers resources for identifying and dating their acoustic guitars, including serial number charts and model histories.
By utilizing these brand-specific resources, you can access accurate and reliable information that will aid in your identification efforts.
13. How To Determine Guitar Value?
Determining the value of your guitar involves several factors, including its make, model, year, condition, and originality. Consulting price guides, checking online marketplaces, and seeking professional appraisals can help you arrive at a reasonable estimate.
Steps to Determine Guitar Value:
- Consult Price Guides: Use resources like the Vintage Guitar Price Guide to get a general idea of your guitar’s value.
- Check Online Marketplaces: Look at websites like Reverb and eBay to see what similar guitars are selling for.
- Assess Condition: Evaluate the condition of your guitar, considering factors like finish wear, hardware condition, and structural integrity.
- Verify Originality: Determine if any parts have been replaced or if any modifications have been made, as these can affect the value.
- Get a Professional Appraisal: Consider hiring a professional appraiser for a more accurate valuation.
By following these steps, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of your guitar’s market value.
14. How To Care For And Maintain Your Guitar After Identifying It?
Proper care and maintenance are essential for preserving the condition and value of your guitar. Regular cleaning, proper storage, and periodic maintenance can help ensure that your instrument remains in top shape for years to come.
Essential Guitar Care Tips:
- Cleaning: Regularly wipe down your guitar with a soft cloth to remove dirt and fingerprints. Use guitar-specific cleaning products for a deeper clean.
- Humidity Control: Maintain proper humidity levels to prevent cracking and warping. Use a humidifier or dehumidifier as needed.
- Storage: Store your guitar in a case when not in use to protect it from dust and damage.
- String Changes: Change your strings regularly to maintain optimal sound quality.
- Professional Setup: Have your guitar professionally set up periodically to ensure proper playability.
By following these care and maintenance tips, you can keep your guitar in excellent condition and protect your investment.
15. What Are The Common Mistakes To Avoid When Identifying A Guitar?
Identifying a guitar can be a complex process, and it’s easy to make mistakes along the way. Avoiding common pitfalls can help ensure that you arrive at an accurate identification.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Relying Solely on the Serial Number: Serial numbers can be misleading, especially if they have been tampered with or misinterpreted.
- Ignoring Physical Features: Overlooking important physical features like the body shape, finish, and hardware can lead to incorrect identification.
- Failing to Research: Not conducting thorough research on the guitar’s history and specifications can result in inaccurate conclusions.
- Ignoring Expert Advice: Dismissing the opinions of experts and experienced guitar enthusiasts can lead to missed clues and incorrect assessments.
- Assuming Originality: Always verify the originality of the guitar and its components, as modifications can significantly impact its value and identity.
By being aware of these common mistakes, you can approach the identification process with greater caution and accuracy.
16. What Are Some Famous Guitar Brands And Their Identifying Characteristics?
Understanding the identifying characteristics of famous guitar brands can greatly assist in the identification process. Each brand has unique features that set its instruments apart.
Famous Guitar Brands and Their Characteristics:
- Fender: Known for bolt-on necks, single-coil pickups, and iconic models like the Stratocaster and Telecaster.
- Gibson: Famous for set necks, humbucker pickups, and legendary models like the Les Paul and SG.
- Martin: Renowned for high-quality acoustic guitars with distinctive bracing patterns and rich tonal qualities.
- Gretsch: Known for their hollow-body guitars with unique aesthetics and Filter’Tron pickups.
- Rickenbacker: Famous for their distinctive jangle tone and unique body shapes, often used by bands like The Beatles.
By familiarizing yourself with these brands and their characteristics, you can more easily identify guitars and understand their historical significance.
17. How Does Guitarplayers.Net Help In Identifying And Learning About Guitars?
Guitarplayers.net is a valuable resource for guitar enthusiasts looking to identify and learn more about their instruments. The site offers a wealth of information, including articles, forums, and expert advice, to assist you in your guitar journey.
How Guitarplayers.net Can Help:
- Comprehensive Articles: Access detailed articles on guitar identification, maintenance, and history.
- Active Forums: Connect with a community of knowledgeable guitar enthusiasts who can offer insights and advice.
- Expert Reviews: Read reviews and comparisons of different guitar models to help you understand their features and values.
- Learning Resources: Find tutorials and lessons to improve your guitar playing skills.
Guitarplayers.net provides a supportive and informative environment for guitar enthusiasts of all levels.
Address: 1140 Boylston Street, Boston, MA 02215, United States
Phone: +1 (617) 747-2261
Website: guitarplayers.net
18. What Are The Different Types Of Guitar Construction?
Understanding the different types of guitar construction can help you identify and appreciate the nuances of your instrument. The construction method affects the guitar’s tone, playability, and overall quality.
Common Types of Guitar Construction:
- Bolt-On Neck: The neck is attached to the body with screws. Common in Fender guitars, this construction offers a bright, articulate tone.
- Set Neck: The neck is glued to the body. Common in Gibson guitars, this construction provides a warm, sustained tone.
- Neck-Through-Body: The neck extends through the entire length of the body. This construction offers maximum sustain and stability.
- Acoustic Guitar Bracing: Different bracing patterns, such as X-bracing and fan bracing, affect the acoustic guitar’s sound projection and tonal balance.
By understanding these construction methods, you can better assess the quality and characteristics of your guitar.
19. What Are The Most Common Types Of Wood Used In Guitars?
The type of wood used in a guitar’s construction significantly impacts its tone and playability. Different woods have different densities and tonal properties, making them suitable for various parts of the instrument.
Common Guitar Woods:
- Alder: A balanced tonewood used in many Fender guitars, known for its clear and resonant sound.
- Mahogany: A warm and resonant wood used in Gibson guitars, providing a rich and sustained tone.
- Maple: A bright and articulate wood used for necks and tops, offering a clear and focused sound.
- Rosewood: A dense wood used for fretboards, providing a smooth playing surface and warm tonal characteristics.
- Spruce: A common top wood for acoustic guitars, known for its bright and dynamic sound projection.
Understanding the tonal properties of these woods can help you identify and appreciate the unique sound of your guitar.
20. What Are The Key Differences Between Acoustic, Electric, And Bass Guitars?
Acoustic, electric, and bass guitars serve different musical purposes and have distinct construction and tonal characteristics. Understanding these differences is essential for any guitar enthusiast.
Key Differences:
- Acoustic Guitars: Produce sound through the vibration of the strings and the resonating body. They have a hollow body and are typically made of wood.
- Electric Guitars: Use pickups to convert the vibration of the strings into an electrical signal, which is then amplified. They can be solid-body, semi-hollow, or hollow-body.
- Bass Guitars: Designed to play lower frequencies, typically with four or five strings. They have a longer scale length and heavier strings than standard guitars.
Each type of guitar offers unique tonal possibilities and playing experiences, catering to different musical styles and preferences.
21. What Are Some Notable Guitar Innovations And Their Impact?
Throughout the history of the guitar, numerous innovations have shaped the instrument and influenced musical styles. Understanding these innovations can provide valuable context when identifying and appreciating your guitar.
Notable Guitar Innovations:
- Electric Pickups: Revolutionized guitar playing by allowing instruments to be amplified, leading to the development of rock and roll.
- Humbucker Pickups: Designed to reduce noise and provide a thicker, more powerful tone, popular in rock and metal music.
- Tremolo Systems: Allow players to create vibrato effects, adding expressiveness to their playing.
- Solid-Body Construction: Enabled guitars to be played at higher volumes without feedback, paving the way for modern electric guitar design.
These innovations have transformed the guitar and expanded its sonic possibilities, influencing countless musicians and genres.
22. How To Identify Counterfeit Guitars?
Identifying counterfeit guitars is crucial for protecting yourself from fraud and ensuring that you are getting a genuine instrument. Counterfeit guitars often lack the quality and craftsmanship of authentic models.
Signs of a Counterfeit Guitar:
- Low Price: If the price seems too good to be true, it might be a sign of a counterfeit guitar.
- Poor Craftsmanship: Look for flaws in the finish, hardware, and construction.
- Incorrect Serial Number: Check the serial number against manufacturer databases to ensure it is legitimate.
- Missing Features: Compare the guitar to official specifications and look for any missing or incorrect features.
- Incorrect Logo: Examine the headstock logo for any discrepancies or misspellings.
By being vigilant and aware of these signs, you can avoid purchasing a counterfeit guitar.
23. What To Do With The Guitar Information You Have Found?
Once you have gathered all the information about your guitar, you can use it to enhance your playing experience, connect with other musicians, and preserve the instrument’s history.
How to Use Your Guitar Information:
- Share Your Knowledge: Share your findings with other guitar enthusiasts in online forums or local guitar communities.
- Preserve the Guitar’s History: Document the guitar’s history and provenance for future generations.
- Proper Maintenance: Use your knowledge to properly maintain and care for the guitar.
- Connect with Other Musicians: Use the guitar’s unique characteristics to inspire your playing and connect with musicians who share your passion.
By using the information you have found, you can deepen your appreciation for your guitar and its place in musical history.
24. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Where can I find the serial number on my guitar?
The serial number’s location varies by brand. Look on the back of the headstock (Gibson), neck plate (Fender), or inside the soundhole (acoustic guitars).
Q2: How do I decode the serial number?
Refer to the manufacturer’s serial number guide. Fender and Gibson have guides online; Gruhn’s Guitar Guide is a comprehensive resource.
Q3: What physical features should I examine?
Check the body shape, finish, headstock design, and hardware. These details can help narrow down the model and year.
Q4: How can I check the guitar’s hardware and electronics?
Examine the potentiometers for date codes. The first three digits indicate the manufacturer, and the following digits represent the year and week of manufacture.
Q5: What online resources can help me research my guitar?
Guitar forums (Fender Forum, Gibson Forum) and vintage guitar databases (Vintage Guitar Magazine) offer valuable information.
Q6: How do modifications affect the value of my guitar?
Original, unmodified guitars are generally more valuable. Replacement pickups, refinishing, and hardware changes can decrease the value.
Q7: What are some common mistakes to avoid when identifying a guitar?
Relying solely on the serial number, ignoring physical features, and failing to research are common mistakes.
Q8: How can Guitarplayers.net help me?
Guitarplayers.net offers articles, forums, and expert advice to help you identify and learn about your guitar.
Q9: What are the key differences between acoustic, electric, and bass guitars?
Acoustic guitars produce sound through the body’s resonance, electric guitars use pickups and amplification, and bass guitars play lower frequencies.
Q10: How can I identify counterfeit guitars?
Look for a low price, poor craftsmanship, incorrect serial number, missing features, and an incorrect logo.
Visit guitarplayers.net to explore lessons, reviews, and connect with a vibrant community of guitar lovers. Start your musical journey today!
