Are you ready to unlock the secrets of musical notation and elevate your guitar playing? Learning how to read guitar sheet music is an essential skill for any guitarist, and at guitarplayers.net, we’re here to guide you through every step of the process. Understanding sheet music, guitar tabs, and chord charts will open up a world of musical possibilities, from mastering your favorite songs to composing your own melodies. Let’s explore the different types of guitar sheet music and how to read them, empowering you to become a more versatile and accomplished guitar player, and remember to use the resources we offer at guitarplayers.net like lessons, songbooks and online community.
1. Understanding Guitar Sheet Music: An Overview
What exactly constitutes “guitar sheet music,” and why is it important?
Guitar sheet music is a broad term that encompasses various forms of notation used to represent music for the guitar. It’s important because it allows guitarists to learn and play music accurately, expand their musical knowledge, and communicate with other musicians.
There are three primary types: tablature (guitar tabs), chord boxes, and traditional musical notation. Let’s dive into each one.
1.1. Tablature (Guitar Tabs): The Guitarist’s Go-To
What is tablature, and why is it so popular among guitarists?
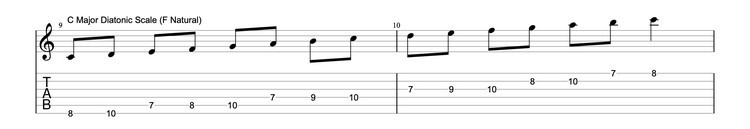
Tablature, or “guitar tabs,” is a simplified form of musical notation specifically designed for guitarists. It uses numbers and lines to represent the fret and string that should be played, making it easy to learn songs without prior musical knowledge. Its popularity stems from its user-friendliness and accessibility.
- Visual Representation: Guitar tabs offer a visual representation of the guitar fretboard, making it easier to understand where to place your fingers.
- Accessibility: No need for formal music training; anyone can pick up a tab and start playing.
- Wide Availability: Countless songs are available in tab format online, making it easy to learn your favorites.
 Guitar Tablature Example: Easy-to-read guitar tablature demonstrating basic notes on the fretboard
Guitar Tablature Example: Easy-to-read guitar tablature demonstrating basic notes on the fretboard
1.2. Chord Boxes: Your Visual Chord Dictionary
What are chord boxes, and how do they simplify chord learning?
Chord boxes are diagrams that illustrate the finger placement for guitar chords. They provide a visual representation of the guitar neck, showing you exactly where to put your fingers to form a chord. They are useful in simplifying chord learning by offering a quick and easy reference for chord shapes.
- Visual Aid: Chord boxes are a visual representation of the fretboard, making it easy to see where your fingers should go.
- Beginner-Friendly: Perfect for beginners who are just starting to learn chords.
- Quick Reference: Chord boxes provide a quick and easy way to look up chord shapes.
1.3. Traditional Musical Notation: The Comprehensive Approach
Why should guitarists bother with traditional musical notation, even if it seems daunting?
Traditional musical notation, also known as “sheet music,” is a comprehensive system of writing music that uses symbols and a staff to represent pitch, rhythm, and other musical elements. While it can seem daunting at first, learning to read traditional notation opens up a world of musical possibilities. Guitarists should consider it because it provides a deeper understanding of music theory, enhances their ability to communicate with other musicians, and allows them to play a wider range of musical styles.
- Comprehensive: Traditional notation provides a complete picture of the music, including rhythm, melody, and harmony.
- Versatile: It can be used to represent any type of music, from classical to jazz to pop.
- Communication: Knowing traditional notation allows you to communicate with other musicians who may not read tabs.
2. Decoding Guitar Tablature: A Step-by-Step Guide
How can you decipher the lines and numbers of guitar tabs to play your favorite songs?
Guitar tablature can be easily deciphered by understanding that each line represents a string on the guitar, and the numbers indicate which fret to play on that string. Read the tab from left to right, playing the notes in sequence.
2.1. Understanding the Lines and Numbers
What do the lines and numbers on a guitar tab actually represent?
In guitar tabs, each of the six lines corresponds to one of the six strings on a guitar. The top line represents the high E string (the thinnest string), while the bottom line represents the low E string (the thickest string). Numbers on the lines indicate which fret to press down on that particular string. A “0” means to play the open string.
- String Order: The lines are arranged in the same order as the strings on your guitar, making it easy to visualize.
- Fret Numbers: The numbers tell you exactly which fret to press down.
- Open Strings: A “0” indicates that you should play the string without pressing down on any fret.
2.2. Reading the Tab: Left to Right
Why is it important to read guitar tabs from left to right?
Reading guitar tabs from left to right is crucial because it indicates the sequence in which the notes should be played, mirroring the flow of music in time. This method ensures that you play the notes in the correct order, which is essential for reproducing the intended melody or riff.
2.3. Example Tablature: A Simple Progression
Let’s analyze a simple tab to understand how to read guitar sheet music effectively.
Consider the following tab:
e|---------------------------|
B|---------------------------|
G|---------------------------|
D|---------------------------|
A|--------0--2--4--2--0------|
E|--0--2-----------------2--0|This tab shows a simple progression:
- E string, 0: Play the open low E string.
- E string, 2: Press down on the 2nd fret of the low E string.
- A string, 0: Play the open A string.
- A string, 2: Press down on the 2nd fret of the A string.
- A string, 4: Press down on the 4th fret of the A string.
- A string, 2: Press down on the 2nd fret of the A string.
- A string, 0: Play the open A string.
- E string, 2: Press down on the 2nd fret of the low E string.
- E string, 0: Play the open low E string.
3. Chord Boxes Demystified: Visualizing Chord Shapes
How do chord boxes help you quickly learn and play new guitar chords?
Chord boxes help you quickly learn and play new guitar chords by providing a visual representation of the fretboard and finger placements. They demystify the process by showing you exactly where to put your fingers to create a specific chord.
3.1. Anatomy of a Chord Box
What are the key elements of a chord box, and what do they represent?
The key elements of a chord box include vertical lines representing the guitar strings, horizontal lines representing the frets, dots indicating finger placement, and symbols like “X” and “O” representing strings that should not be played or played open, respectively.
- Vertical Lines: Represent the strings of the guitar, with the leftmost line being the low E string and the rightmost line being the high E string.
- Horizontal Lines: Represent the frets on the guitar.
- Dots: Indicate where you should place your fingers on the fretboard. The numbers inside the dots typically indicate which finger to use (1=index, 2=middle, 3=ring, 4=pinky).
- X: Indicates that the string should not be played.
- O: Indicates that the string should be played open.
3.2. Finger Placement: The Numbering System
How does the numbering system in chord boxes help with finger placement?
The numbering system in chord boxes corresponds to your fingers: 1 for index, 2 for middle, 3 for ring, and 4 for pinky. This system guides you on which finger to use for each note, making it easier to form the chord correctly.
3.3. Example Chord Box: C Major
Let’s break down a C Major chord box to illustrate how to read it.
 C Major Chord Box: A diagram showing the finger placement for a C Major chord
C Major Chord Box: A diagram showing the finger placement for a C Major chord
In this chord box:
- The “X” above the low E string indicates that you should not play that string.
- The “O” above the G string indicates that you should play that string open.
- The numbers on the dots tell you which finger to use:
- 1 (index finger) on the B string, 1st fret.
- 2 (middle finger) on the D string, 2nd fret.
- 3 (ring finger) on the A string, 3rd fret.
4. Traditional Notation for Guitar: Delving Deeper
Why should guitarists learn traditional notation, and how does it enhance their musical understanding?
Learning traditional notation enhances a guitarist’s musical understanding by providing a comprehensive system for reading and interpreting music. It allows guitarists to understand the theory behind the music, communicate with other musicians, and play a wider range of musical styles accurately.
4.1. The Staff, Clef, and Notes
What are the basic elements of traditional notation, and what do they signify?
The basic elements of traditional notation are the staff (five lines and four spaces), the clef (which indicates the pitch of the notes), and the notes themselves (which represent specific pitches and durations).
- Staff: The five lines and four spaces on which the notes are written.
- Clef: A symbol at the beginning of the staff that indicates the pitch of the notes. The most common clef for guitar is the treble clef.
- Notes: Symbols that represent specific pitches and durations. The position of the note on the staff indicates its pitch, while the shape of the note indicates its duration.
4.2. Rhythm and Time Signatures
How do rhythm and time signatures work in traditional notation?
Rhythm in traditional notation is indicated by the shape of the notes (whole, half, quarter, etc.) and their placement on the staff, while time signatures indicate the number of beats per measure and the type of note that receives one beat.
- Note Values: Different note shapes represent different durations. A whole note lasts for four beats, a half note lasts for two beats, a quarter note lasts for one beat, and so on.
- Time Signatures: A time signature consists of two numbers, one above the other. The top number indicates the number of beats per measure, while the bottom number indicates the type of note that receives one beat. For example, a 4/4 time signature means there are four beats per measure, and a quarter note receives one beat.
4.3. Sharps, Flats, and Naturals
What do sharps, flats, and naturals do to notes on the staff?
Sharps (♯) raise the pitch of a note by a half step, flats (♭) lower the pitch by a half step, and naturals (♮) cancel the effect of a sharp or flat. These symbols alter the pitch of a note, allowing for a wider range of musical expression.
5. Techniques and Symbols in Guitar Sheet Music
How are advanced guitar techniques represented in tablature and traditional notation?
Advanced guitar techniques are represented in tablature and traditional notation through various symbols and notations, such as hammer-ons, pull-offs, bends, slides, and palm muting.
5.1. Hammer-Ons and Pull-Offs
How are hammer-ons and pull-offs indicated in guitar tabs and sheet music?
Hammer-ons and pull-offs are often indicated in guitar tabs using “h” for hammer-ons (e.g., 7h9) and “p” for pull-offs (e.g., 9p7). They can also be represented with a curved line connecting the two notes. In traditional notation, they may be indicated with a slur (curved line) over the notes.
5.2. String Bends and Slides
What symbols are used to represent string bends and slides in guitar sheet music?
String bends are typically indicated with a “b” between two fret numbers (e.g., 12b14), indicating that the string should be bent from the 12th fret to the pitch of the 14th fret. Slides are represented with a forward slash (/) for sliding up and a backslash () for sliding down (e.g., 5/75).
5.3. Muting Techniques
How is muting, including palm muting, notated in guitar sheet music?
Muting is displayed using X’s, whereas palm muting is displayed with a ‘PM’ above the top tab line.
6. Comparing the Three Types: A Practical Example
How do tablature, chord boxes, and traditional notation compare when representing the same musical idea?
Tablature, chord boxes, and traditional notation each represent musical ideas differently. Tablature provides a direct, visual guide to fretboard positions, chord boxes offer a snapshot of finger placements for chords, and traditional notation gives a comprehensive view of pitch, rhythm, and harmony.
6.1. C Major Chord: Three Perspectives
Let’s examine how a C Major chord is represented in each format.
- Tablature:
e|--0--|
B|--1--|
G|--0--|
D|--2--|
A|--3--|
E|--x--|-
Chord Box: (See the chord box image above)
-
Traditional Notation: (A musical staff with the notes C, E, and G appropriately placed)
6.2. Pros and Cons: Choosing the Right Method
What are the advantages and disadvantages of each type of guitar sheet music?
- Tablature:
- Pros: Easy to read, beginner-friendly, widely available.
- Cons: Lacks rhythmic information, doesn’t convey musical theory.
- Chord Boxes:
- Pros: Visual, quick reference for chords.
- Cons: Limited information, doesn’t show melody or rhythm.
- Traditional Notation:
- Pros: Comprehensive, includes all musical information, enhances musical understanding.
- Cons: Requires musical knowledge, can be difficult for beginners.
7. Tips for Mastering Guitar Sheet Music
What are some effective strategies for improving your ability to read and play guitar sheet music?
Effective strategies include practicing regularly, starting with simple pieces, focusing on rhythm, learning music theory, and utilizing online resources and communities.
7.1. Practice Regularly
How important is consistent practice for improving your sheet music reading skills?
Consistent practice is essential for improving your sheet music reading skills. Regular practice helps you internalize the symbols and notations, develop muscle memory, and improve your overall musicality.
7.2. Start Simple
Why should beginners start with simple pieces when learning to read guitar sheet music?
Starting with simple pieces allows beginners to focus on the fundamentals of reading and playing without being overwhelmed by complex rhythms or techniques. It builds confidence and reinforces basic concepts.
7.3. Focus on Rhythm
How can you improve your rhythmic accuracy when reading guitar sheet music?
You can improve your rhythmic accuracy by using a metronome, counting out loud, and clapping or tapping the rhythm before playing. Understanding time signatures and note values is also crucial.
7.4. Learn Music Theory
How does learning music theory enhance your ability to read and understand guitar sheet music?
Learning music theory provides a deeper understanding of the underlying structure of music, making it easier to recognize patterns, predict chord progressions, and understand the relationship between melody and harmony.
7.5. Utilize Online Resources and Communities
What are some valuable online resources and communities for guitarists learning to read sheet music?
Valuable online resources include websites like guitarplayers.net, which offer lessons, tabs, chord charts, and a community forum for guitarists to connect and learn from each other. Other resources include YouTube tutorials, online music theory courses, and apps for practicing sight-reading.
8. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Learning to read guitar sheet music can present various challenges, but with the right strategies, you can overcome them and improve your skills.
8.1. Recognizing Notes Quickly
Challenge: Difficulty in quickly identifying notes on the staff.
Solution: Practice sight-reading exercises daily, focusing on recognizing intervals and patterns rather than individual notes. Use flashcards or apps to quiz yourself on note recognition.
8.2. Understanding Rhythmic Notation
Challenge: Struggling to interpret complex rhythmic patterns.
Solution: Break down rhythms into smaller, manageable chunks. Use a metronome to practice playing rhythms accurately. Clap or tap rhythms before playing them on the guitar.
8.3. Coordinating Reading and Playing
Challenge: Difficulty coordinating reading sheet music and playing the guitar simultaneously.
Solution: Start with simple exercises that involve playing single notes or basic chords while reading the sheet music. Gradually increase the complexity as your coordination improves.
8.4. Memorizing Symbols and Techniques
Challenge: Forgetting the meaning of various symbols and techniques used in guitar sheet music.
Solution: Create a reference sheet or cheat sheet with explanations of common symbols and techniques. Review this sheet regularly and refer to it when encountering unfamiliar notation.
8.5. Staying Motivated
Challenge: Losing motivation due to the perceived difficulty of learning to read guitar sheet music.
Solution: Set realistic goals and celebrate small victories along the way. Choose pieces of music that you enjoy playing to keep yourself engaged and motivated. Join a guitar community or find a practice partner to share your progress and challenges with.
9. The Benefits of Learning to Read Guitar Sheet Music
Investing time and effort into learning to read guitar sheet music can yield numerous benefits that enhance your musical journey and playing abilities.
9.1. Expanded Musical Knowledge
Benefit: A deeper understanding of music theory, harmony, and composition.
Explanation: Reading sheet music allows you to analyze and interpret musical structures, chord progressions, and melodic patterns, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of music as a whole.
9.2. Improved Communication with Musicians
Benefit: Enhanced ability to communicate with other musicians, regardless of their instrument or background.
Explanation: Traditional sheet music serves as a universal language among musicians, enabling you to collaborate, rehearse, and perform together effectively.
9.3. Access to a Wider Range of Music
Benefit: Unlocking a vast repertoire of music that may not be available in tablature or chord chart format.
Explanation: Many classical, jazz, and contemporary pieces are written in traditional notation, opening up new musical horizons for guitarists who can read sheet music.
9.4. Enhanced Sight-Reading Skills
Benefit: Improved ability to quickly learn and perform new pieces of music on the spot.
Explanation: Regular practice of sight-reading exercises strengthens your ability to recognize notes, rhythms, and musical patterns, enabling you to play music with greater fluency and accuracy.
9.5. Increased Confidence and Versatility
Benefit: Greater confidence in your abilities as a guitarist and increased versatility in various musical styles and settings.
Explanation: Mastering guitar sheet music equips you with the skills and knowledge to tackle a wide range of musical challenges, empowering you to express yourself creatively and confidently on the guitar.
10. Resources at guitarplayers.net to Help You Learn
How can guitarplayers.net assist you in your journey to master guitar sheet music?
guitarplayers.net offers a wealth of resources, including lessons, tabs, chord charts, articles, and a vibrant community forum, all designed to support guitarists of all levels in their musical journey.
- Lessons: Step-by-step guides on reading tabs, chord boxes, and traditional notation.
- Tabs and Chord Charts: A vast library of songs in tab and chord chart format.
- Articles: In-depth articles on music theory, guitar techniques, and more.
- Community Forum: A place to connect with other guitarists, ask questions, and share your progress.
10.1. Explore Our Extensive Song Library
What types of songs and resources can you find in the guitarplayers.net song library?
Our song library offers a wide variety of songs in different genres and skill levels, complete with tabs, chord charts, and even sheet music for some pieces.
10.2. Join Our Community Forum
How can participating in the guitarplayers.net community forum benefit your learning experience?
Participating in our community forum allows you to connect with other guitarists, ask questions, share your progress, and receive feedback. It’s a supportive environment where you can learn from others and stay motivated.
10.3. Take Advantage of Personalized Learning Plans
How does guitarplayers.net tailor learning plans to suit individual guitarists’ needs and goals?
At guitarplayers.net we offer personalized learning plans to tailor learning to suit individual guitarists’ needs and goals. By assessing your current skill level, musical preferences, and learning objectives, we curate a customized curriculum designed to accelerate your progress and help you achieve your full potential on the guitar.
Reading guitar sheet music is a skill that unlocks a world of musical possibilities. Whether you prefer the simplicity of tablature, the visual aid of chord boxes, or the comprehensive approach of traditional notation, mastering these skills will undoubtedly enhance your guitar playing. Start your journey today with guitarplayers.net!
Ready to take your guitar playing to the next level?
- Explore our lessons on reading guitar sheet music.
- Browse our song library for tabs and chord charts.
- Join our community forum to connect with other guitarists.
Visit guitarplayers.net today and discover the joy of reading and playing guitar sheet music! Address: 1140 Boylston Street, Boston, MA 02215, United States. Phone: +1 (617) 747-2261. Website: guitarplayers.net.
 Guitar Sheet Music: A collection of guitar sheet music, symbolizing the vast possibilities that open up when you learn to read music
Guitar Sheet Music: A collection of guitar sheet music, symbolizing the vast possibilities that open up when you learn to read music
FAQ About Reading Guitar Sheet Music
1. What is the first thing I should learn when starting to read guitar sheet music?
Start by learning the basics of tablature (guitar tabs) as it is the most straightforward method for guitarists, then move on to chord boxes, and finally traditional notation.
2. How long does it take to become proficient in reading guitar sheet music?
Proficiency varies, but with consistent daily practice, you can grasp the basics in a few weeks and become reasonably proficient within a few months.
3. Do I need to know music theory to read guitar tabs?
No, you don’t need music theory to read guitar tabs. However, understanding basic music theory can enhance your overall musical understanding and make learning easier.
4. What is the difference between a sharp and a flat in traditional notation?
A sharp (♯) raises a note by a half step, while a flat (♭) lowers a note by a half step.
5. Can I learn to read guitar sheet music online?
Yes, many online resources, including guitarplayers.net, offer lessons, tutorials, and exercises to help you learn to read guitar sheet music.
6. What are some common mistakes beginners make when reading guitar sheet music?
Common mistakes include ignoring rhythmic notation, not using a metronome, and trying to learn too much too soon.
7. Is it necessary to learn traditional notation if I can already read tabs?
While not necessary, learning traditional notation can greatly enhance your musical understanding and open up new musical opportunities.
8. How can I improve my sight-reading skills on the guitar?
Practice sight-reading regularly with new pieces of music, focusing on recognizing patterns and rhythms quickly.
9. What is the best way to memorize chord shapes for chord boxes?
Practice forming the chords repeatedly, visualize the finger placements, and use mnemonic devices to help you remember the shapes.
10. Are there any apps that can help me learn to read guitar sheet music?
Yes, there are several apps available that offer interactive lessons, exercises, and games to help you learn to read guitar sheet music, such as Music Tutor, Teoria, and Functional Ear Trainer.


