Are you curious about how many notes are on a guitar and eager to master the fretboard? At guitarplayers.net, we provide aspiring guitarists and seasoned musicians alike with a comprehensive understanding of guitar notes and fretboard mastery. You will find practical tips, resources, and a supportive community to enhance your musical journey and elevate your guitar-playing skills. Explore scales, chords, and music theory essentials on guitarplayers.net.
1. Understanding the Basics: What is a Note?
Simply put, a note represents the pitch of a sound. Whenever you play a string on your guitar at any fret, you produce a note. These notes are the foundation of melodies, harmonies, and everything else that makes music so captivating.
1.1 The Three Types of Notes: Naturals, Flats, and Sharps
In music theory, there are three primary types of notes: natural, flat, and sharp. Understanding these distinctions is essential for navigating the fretboard and comprehending musical notation.
-
Natural Notes: These are the basic notes in the musical alphabet, represented as A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. A natural note is written simply as its letter. For example, A natural is written as A.
-
Flat Notes: A flat note is slightly lower in pitch than its corresponding natural note. It is typically written with a flat symbol (♭) after the letter, such as A♭ or Ab.
-
Sharp Notes: A sharp note, on the other hand, is slightly higher in pitch than its natural counterpart. It is usually written with a sharp symbol (♯) after the letter, such as A♯ or A#.
To visualize the relationship between flat, natural, and sharp notes, imagine the natural note in the middle, with the flat note to its left (lower in pitch) and the sharp note to its right (higher in pitch):
A♭ – A – A♯
 flat, natural, and sharp notes visualized
flat, natural, and sharp notes visualized
1.2 Using Flats and Sharps to Indicate Pitch Changes
The terms “flat” and “sharp” are also used to describe changes in pitch.
- Flattened: If a note moves down in pitch, it is said to be flattened.
- Sharpened: If a note moves up in pitch, it is said to be sharpened.
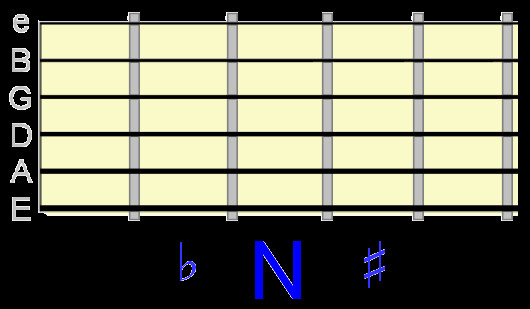
Consider a starting note “N” on any string. Here’s how these changes would appear on the fretboard:
 flat, natural, and sharp notes visualized
flat, natural, and sharp notes visualized
1.3 Understanding Enharmonic Equivalents
According to research from the Berklee College of Music, enharmonic notes are pitches with different names but the same sound. For instance, A♯ and B♭ sound identical, as do C♯ and D♭. Which name you use depends on the musical context. Enharmonic equivalents simplify music theory, but beginners might find it confusing.
2. The Chromatic Scale and the Musical Alphabet on Guitar
The chromatic scale includes all 12 notes used in Western music.
2.1 The 12 Notes of the Chromatic Scale
Just like on a piano, there are 12 notes in total on the guitar, which together form the chromatic scale. This means that every 12 frets on the guitar, starting from any fret on any string, cover the complete range of notes. Starting on the note A, the chromatic scale is:
A – A♯/B♭ – B – C – C♯/D♭ – D – D♯/E♭ – E – F – F♯/G♭ – G – G♯/A♭
The note following G♯/A♭ is A, and the sequence repeats every 12 notes. This sequence is known as the chromatic or 12-tone scale.
2.2 Enharmonic Notes Explained
Pitches with both sharp and flat notations are called enharmonic. For example, A♯ and B♭ are the same pitch (they are enharmonic), as are C♯ and D♭, etc. The choice between sharp or flat depends on the musical context, which you’ll learn as you progress.
2.3 Exceptions to the Rule
Notice that some notes are not separated by sharps or flats, namely B and C, and E and F. This means that a B♯ is actually C, and a C♭ is B. Similarly, E♯ is F.
While it’s less common, there are instances where you would write C and F as B♯ and E♯, respectively. For now, focus on memorizing the natural sequence of notes and applying them to the guitar fretboard.
3. Mapping Notes on the Guitar Fretboard
Let’s start mapping these notes onto the guitar fretboard, beginning with the low E (6th) string.
3.1 Natural Notes on the Low E (6th) String
The low E string is often the starting point for many guitarists. Here are the natural notes on this string:
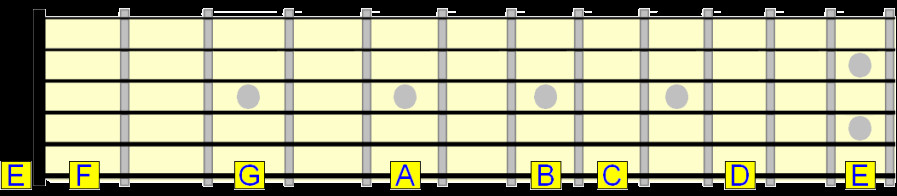 natural notes on the 6th string
natural notes on the 6th string
-
The open E string produces an E note. The 12th fret E is the same note but an octave higher in pitch.
-
F note at the 1st fret
-
G note at the 3rd fret
-
A note at the 5th fret
-
B note at the 7th fret
-
C note at the 8th fret
-
D note at the 10th fret
Remember that the note sequence repeats beyond the 12th fret octave, so the 13th fret will be the octave of (same note as) the 1st fret F. The 17th fret will be the octave of the 5th fret A. Try to locate these note octaves beyond the 12th fret.
3.2 Filling in the Gaps: Sharps and Flats on the Low E String
Now, let’s fill in the gaps with the sharps and flats:
-
F sharp / G flat at the 2nd fret
-
G sharp / A flat at the 4th fret
-
A sharp / B flat at the 6th fret
-
C sharp / D flat at the 9th fret
-
D sharp / E flat at the 11th fret
3.3 Natural Notes on the A (5th) String
Moving on to the A (5th) string, let’s identify the natural notes, starting from the open A string:
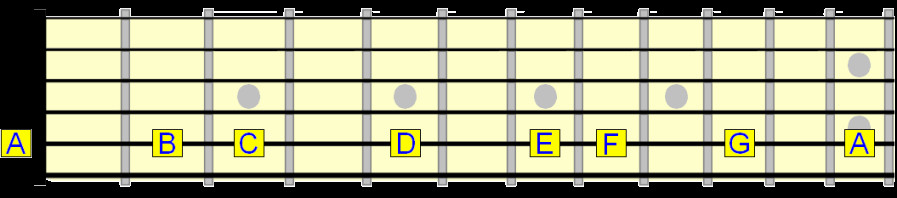 natural notes on the 5th string
natural notes on the 5th string
-
A note on the open string. The 12th fret A is an octave higher.
-
B note at the 2nd fret
-
C note at the 3rd fret
-
D note at the 5th fret
-
E note at the 7th fret
-
F note at the 8th fret
-
G note at the 10th fret
3.4 Filling in the Gaps: Sharps and Flats on the A String
Fill in the flat/sharp gaps on the A string as follows:
-
A sharp / B flat at the 1st fret
-
C sharp / D flat at the 4th fret
-
D sharp / E flat at the 6th fret
-
F sharp / G flat at the 9th fret
-
G sharp / A flat at the 11th fret
3.5 Applying the Method to Other Strings
You can use the same method to memorize the notes on the remaining strings (D, G, B, and high E). The high E string has the same sequence of notes as the low E string, but two octaves higher.
4. Complete Fretboard Diagram
Below is a comprehensive diagram showing all the notes on the fretboard, with fret numbers indicated below:
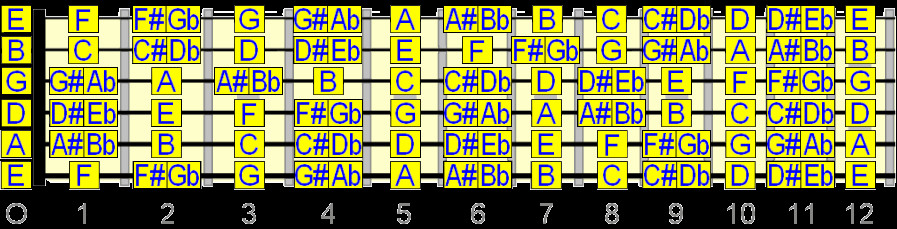 full fretboard notes
full fretboard notes
4.1 Tips for Memorizing Fretboard Notes
Memorizing all the notes on the guitar fretboard can seem daunting, but with consistent practice and effective strategies, it becomes manageable.
-
Start with Natural Notes: Begin by memorizing the natural notes (A, B, C, D, E, F, G) on each string. Focus on one string at a time, and gradually expand your knowledge to the entire fretboard.
-
Use Visual Aids: Diagrams and charts that display the fretboard notes can be incredibly helpful. Keep a chart handy while practicing, and refer to it whenever you need a reminder.
-
Practice Regularly: Consistency is key to memorization. Set aside some time each day to practice identifying notes on the fretboard. Even a few minutes of focused practice can make a significant difference over time.
-
Use Flashcards: Create flashcards with note names on one side and the corresponding fretboard position on the other. This can be a fun and effective way to test your knowledge and reinforce your memory.
-
Play Scales and Arpeggios: Practicing scales and arpeggios is not only great for technique but also helps you become more familiar with the notes on the fretboard. Pay attention to the notes you are playing and try to visualize their positions as you move through the scale.
-
Learn Songs: Choose simple songs that you enjoy playing and focus on identifying the notes as you play them. This will help you connect the notes to actual music and make the learning process more engaging.
-
Use Mnemonics: Create memorable phrases or acronyms to help you remember the order of the notes. For example, “Every Good Boy Does Fine” can help you remember the notes on the lines of the treble clef (E, G, B, D, F).
-
Online Tools: Many online tools and apps can assist you in memorizing the fretboard notes. These tools often include interactive exercises and quizzes that can make learning more fun and effective. One example is the fretboard trainer available at GuitarTricks.
4.2 Practical Exercise for Fretboard Mastery
To test your knowledge, try this exercise: Pick any note and try to locate it on all six strings. You’ll be slow at first, but with practice, your note identification will become quicker and more automatic.
5. The Importance of Fretboard Knowledge for Guitar Players
Knowing the notes on the guitar fretboard is essential for any serious guitar player. It enhances your understanding of music theory, improves your improvisation skills, and makes learning new songs easier.
5.1 Enhancing Music Theory Understanding
Understanding the notes on the fretboard is crucial for comprehending music theory. Knowing the notes helps you understand how chords and scales are constructed.
5.2 Improving Improvisation Skills
Knowing the notes on the fretboard allows you to improvise more freely and confidently. When you know the notes, you can easily find the right notes to play over any chord progression.
5.3 Simplifying Song Learning
Knowing the notes on the fretboard makes learning new songs much easier. Instead of relying solely on tabs or chord diagrams, you can quickly identify the notes being played and understand the underlying harmony.
6. Advanced Concepts: Beyond the Basics
Once you have a solid grasp of the basics, you can start exploring more advanced concepts.
6.1 Understanding Different Guitar Tunings
While standard tuning (EADGBE) is the most common, many guitarists experiment with alternative tunings to achieve different sounds and voicings. Knowing the notes on the fretboard in standard tuning will help you adapt to other tunings more easily.
6.2 Exploring Chord Construction
Understanding how chords are constructed is essential for songwriting and arranging. Knowing the notes on the fretboard allows you to visualize chord shapes and understand how they are formed.
6.3 Mastering Scales and Modes
Scales and modes are essential tools for improvisation and soloing. Knowing the notes on the fretboard allows you to play scales and modes in any key and position.
7. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Learning the notes on the guitar fretboard can be challenging, but with the right approach, you can overcome these obstacles.
7.1 Overcoming Initial Frustration
It’s common to feel overwhelmed when first learning the fretboard notes. Be patient and persistent, and remember that progress takes time.
7.2 Developing Effective Practice Habits
Consistent practice is essential for mastering the fretboard. Set realistic goals, create a practice schedule, and stick to it.
7.3 Utilizing Resources and Seeking Guidance
There are many resources available to help you learn the fretboard notes, including books, websites, and online courses. Don’t hesitate to seek guidance from experienced guitar players or instructors.
8. Resources at GuitarPlayers.net
GuitarPlayers.net offers a variety of resources to help you learn the notes on the guitar fretboard and improve your playing skills.
8.1 Lessons and Tutorials
We provide lessons and tutorials for all levels, covering topics such as fretboard memorization, music theory, and improvisation.
8.2 Fretboard Diagrams and Charts
Our website features detailed fretboard diagrams and charts that you can use as references while practicing.
8.3 Community Forum
Join our community forum to connect with other guitar players, ask questions, and share your progress.
Address: 1140 Boylston Street, Boston, MA 02215, United States. Phone: +1 (617) 747-2261. Website: guitarplayers.net.
9. Expert Opinions on Guitar Learning
According to Guitar World, consistent practice and a structured approach are key to mastering the guitar fretboard. Guitar Player Magazine emphasizes the importance of understanding music theory to enhance your playing skills. These expert opinions highlight the value of dedication and knowledge in guitar learning.
10. Latest Trends in Guitar Education in the USA
| Trend | Description | Impact on Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Online Guitar Lessons | Increase in virtual guitar lessons via platforms like Zoom and Skype. | Greater accessibility and flexibility in learning. |
| App-Based Learning | Guitar learning apps with interactive exercises and personalized feedback. | More engaging and efficient practice sessions. |
| Hybrid Learning Models | Combination of online resources with in-person lessons. | Comprehensive learning experience. |
| Focus on Mental Wellness | Incorporating mindfulness and stress-reduction techniques in guitar education. | Improved focus, reduced anxiety, and better performance. |
| Emphasis on Creativity | Encouraging students to explore songwriting, improvisation, and unique playing styles. | Fosters individuality and creativity in playing. |
| Community-Based Learning | Joining local guitar groups or online communities to learn from peers. | Provides support, motivation, and collaborative opportunities. |
| Personalized Learning Paths | Tailoring instruction to meet individual student needs and goals. | More effective and customized learning experience. |
| Gamification of Learning | Using game-like elements to make practice sessions more enjoyable. | Increases engagement and motivation to practice. |
| Integration of Technology | Utilizing tools like digital audio workstations (DAWs) for recording, composing, and experimenting with music. | Enhances creativity and provides new avenues for musical expression. |
| Focus on Diverse Genres | Exploring a wider range of musical genres beyond traditional rock and blues. | Expands musical knowledge and versatility. |
| Emphasis on Ear Training | Developing the ability to recognize and play musical intervals, chords, and melodies by ear. | Enhances musicality and improvisation skills. |
| Incorporating Music Theory | Integrating music theory concepts into practical guitar instruction. | Provides a deeper understanding of music and enhances analytical skills. |
| Performance Opportunities | Encouraging students to perform in recitals, open mics, and other venues. | Builds confidence and provides practical performance experience. |
| Use of Social Media | Utilizing platforms like YouTube, Instagram, and TikTok for guitar tutorials and performance showcases. | Provides access to vast amounts of free content and opportunities to connect with others. |
11. FAQ: Mastering the Guitar Fretboard
11.1 How many notes are there on a standard guitar?
There are approximately 120-144 notes on a standard 20-24 fret guitar, considering all strings and frets.
11.2 How can I quickly memorize the notes on the fretboard?
Start with natural notes on the E and A strings, use mnemonics, and practice regularly.
11.3 What is the chromatic scale, and how does it relate to the guitar?
The chromatic scale includes all 12 notes in Western music. On the guitar, it means every fret represents a note in this scale.
11.4 Are there any patterns I can use to learn the notes?
Yes, the CAGED system and patterns within scales and chords can help you learn note positions.
11.5 Why is it important to know the notes on the fretboard?
Knowing the notes improves your music theory understanding, improvisation, and ability to learn songs.
11.6 How do sharps and flats affect the notes on the guitar?
Sharps raise a note by a half step, while flats lower it by a half step. They fill in the gaps between natural notes.
11.7 Can alternative tunings change the number of notes on the guitar?
Alternative tunings don’t change the number of notes but alter their positions on the fretboard.
11.8 What are some common mistakes to avoid when learning the fretboard?
Avoid rote memorization without understanding, neglecting practice, and not using resources like diagrams and charts.
11.9 How can I use online resources to improve my fretboard knowledge?
Use online tools like fretboard trainers, lessons, and community forums to enhance your learning.
11.10 Is it necessary to know all the notes on the fretboard to become a good guitar player?
While not strictly necessary, knowing the notes significantly enhances your musical abilities and potential as a guitarist.
12. Take Action Now
Ready to take your guitar playing to the next level? Visit guitarplayers.net today to explore our lessons, find sheet music, read reviews, and join our community. Start your journey to fretboard mastery now and unlock your full potential as a guitarist!

