Identifying chords on guitar can be tricky, but guitarplayers.net offers a streamlined path to mastery for guitarists of all levels. By understanding chord construction, scale relationships, and contextual clues, you can confidently decipher any chord progression, while we provide the resources to help you along the way. Explore diverse lessons, reviews, sheet music, and a community forum, making your guitar journey both enriching and enjoyable.
1. Understanding Chord Fundamentals
Identifying chords on guitar begins with a strong grasp of music theory. Let’s break down the core concepts that will empower you to recognize and name chords effectively.
1.1. The Root Note: The Chord’s Foundation
The name of a chord is derived from its root note, which is the fundamental note upon which the chord is built. Think of the root note as the anchor of the chord. For example, a C major chord has C as its root, an A minor chord has A as its root, and so on. It’s the starting point for understanding the chord’s structure.
1.2. Chord Quality: Unveiling the Character
Chord quality refers to the specific flavor or character of a chord. Common chord qualities include major, minor, diminished, augmented, and seventh. The quality is determined by the intervals (distances between notes) relative to the root note.
- Major chords: Generally sound happy and bright.
- Minor chords: Often convey a sad or melancholic feeling.
- Diminished chords: Create tension and instability.
- Augmented chords: Possess a dissonant, unsettling quality.
- Seventh chords: Add complexity and richness to the harmony.
According to research from the Berklee College of Music, understanding chord qualities helps musicians add depth and emotion to their playing, making their music more engaging.
1.3. Intervals: The Building Blocks of Chords
Intervals are the distances between two notes. Understanding intervals is crucial for determining chord quality. The most important intervals for chord construction are:
- Major third: Two whole steps above the root.
- Minor third: One and a half steps above the root.
- Perfect fifth: Three and a half steps above the root.
For example, a major chord consists of a root, a major third, and a perfect fifth. A minor chord consists of a root, a minor third, and a perfect fifth.
1.4. The Major Scale: A Chord’s Blueprint
The major scale is the foundation for understanding chord construction. By understanding the relationship between the notes of a chord and the major scale of its root, you can determine the chord’s quality.
- Major Chord Formula: 1 (Root), 3 (Major Third), 5 (Perfect Fifth)
- Minor Chord Formula: 1 (Root), b3 (Minor Third), 5 (Perfect Fifth)
- Dominant 7th Chord Formula: 1 (Root), 3 (Major Third), 5 (Perfect Fifth), b7 (Minor Seventh)
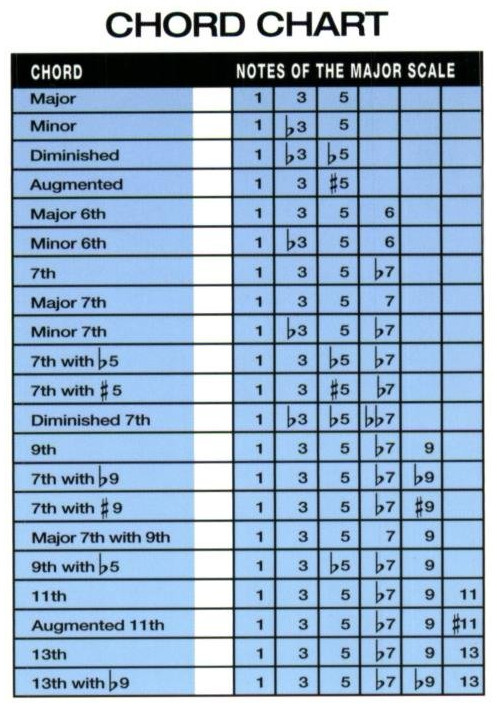 Chord Formation Chart
Chord Formation Chart
2. Overcoming Guitar-Specific Challenges
The guitar presents unique challenges when it comes to identifying chords compared to instruments like the piano. Understanding these challenges and how to overcome them is essential for any guitarist.
2.1. Multiple Positions, Same Pitch
Unlike a piano, where each key produces a unique pitch, the guitar allows you to play the same pitch in multiple locations on the fretboard. This can make it difficult to visually identify the root note and the intervals within a chord.
2.2. Identifying the Root Note on Guitar
The guitar’s layout can obscure the root note within a chord shape. Here are a few tricks to help you locate it:
- Power Chords: These two or three note chords consist of the root note, a perfect fifth, and sometimes an octave of the root. The lowest note is always the root.
- Listen Carefully: Pay attention to the bass notes in the chord. The lowest note you hear is often the root.
- Chord Diagrams: Chord diagrams visually represent the fretboard and finger positions for a particular chord. They usually indicate the root note with a specific symbol.
2.3. Visualizing Intervals on the Fretboard
Developing the ability to visualize intervals on the fretboard is crucial for identifying chords. Start by learning the intervals from the root note on each string. As you become more familiar with the fretboard, you’ll be able to quickly identify the intervals within any chord shape.
2.4. Common Guitar Chord Voicings
Familiarize yourself with common guitar chord voicings (different ways to play the same chord). Knowing these voicings will help you quickly recognize familiar chord shapes and identify the notes they contain.
3. Identifying Chords in Context
While understanding music theory and fretboard knowledge is important, identifying chords in the context of a song is crucial. Here’s how to use musical context to your advantage.
3.1. Chord Function in a Song
The function of a chord within a song provides clues to its identity. Chords don’t exist in isolation; they function within a chord progression that supports the melody and harmony of the song.
3.2. Recognizing Common Chord Progressions
Many songs rely on common chord progressions. Recognizing these progressions can help you quickly identify the chords being played. Some of the most common chord progressions include:
- I-IV-V: A foundational progression in many genres.
- I-V-vi-IV: A popular progression known for its pleasing sound.
- ii-V-I: A common jazz progression that creates a strong sense of resolution.
According to Guitar World Magazine, familiarity with common chord progressions allows guitarists to anticipate chord changes and improve their improvisation skills.
3.3. Analyzing the Melody for Clues
The melody of a song often provides clues about the underlying chords. The notes of the melody tend to emphasize notes within the chords being played.
3.4. Key Signatures and Chord Choices
The key signature of a song limits the number of possible chords that are likely to be used. In the key of C Major, the most common chords will be based on the notes C, D, E, F, G, A, and B.
3.5. Understanding Chord Voicings and Inversions
- Chord Voicings: The specific arrangement of notes in a chord. Different voicings can create subtle variations in sound.
- Chord Inversions: Occur when a note other than the root is the lowest note in the chord.
Understanding inversions helps you identify chords even when they don’t appear in their standard form.
4. Practical Techniques for Chord Identification
Here are some practical techniques you can use to improve your chord identification skills.
4.1. Ear Training Exercises
Ear training is the ability to recognize musical elements, such as intervals, chords, and melodies, by ear. Regular ear training exercises can significantly improve your chord identification skills.
4.2. Transcribing Music
Transcribing music involves listening to a song and writing down the notes, chords, and rhythms you hear. This is a great way to develop your ear and your understanding of how chords function in real musical situations.
4.3. Using a Chord Naming Tool
Online chord naming tools can be helpful for identifying chords you’re unfamiliar with. These tools allow you to input the notes you’re playing and will identify the most likely chord name. One such tool is available at jguitar.com/chordname.
4.4. Analyzing Chord Charts and Sheet Music
Analyzing chord charts and sheet music can help you understand how chords are used in different songs and genres. Pay attention to the chord symbols, the key signatures, and the overall structure of the song.
4.5. Practice Identifying Chords in Different Genres
Different genres of music tend to use different chord progressions and chord voicings. Practicing identifying chords in a variety of genres will broaden your musical vocabulary and improve your overall chord identification skills.
5. Advanced Chord Identification Techniques
Once you have a solid foundation in the basics, you can move on to more advanced chord identification techniques.
5.1. Recognizing Altered Chords
Altered chords contain notes that have been altered (raised or lowered) from the major scale. These chords add color and complexity to the harmony. Common altered chords include:
- Dominant 7b9: A dominant 7th chord with a flattened 9th.
- Dominant 7#9: A dominant 7th chord with a sharpened 9th.
- Altered Dominant Chords: Dominant chords with altered 5ths and 9ths.
5.2. Identifying Slash Chords
Slash chords are chords that have a different bass note than the root. For example, a C/G chord is a C major chord with a G in the bass. Slash chords are often used to create smooth bass lines or to add harmonic interest.
5.3. Understanding Modal Interchange
Modal interchange involves borrowing chords from parallel keys or modes to create harmonic variety. This technique can add unexpected colors and textures to your chord progressions.
5.4. Analyzing Complex Chord Progressions
Some songs feature complex chord progressions that can be challenging to analyze. When faced with a complex progression, try to break it down into smaller sections and identify the function of each chord within the section.
5.5. Exploring Jazz Harmony
Jazz harmony is known for its sophisticated chord voicings and progressions. Exploring jazz harmony can significantly expand your understanding of chord identification and musical theory.
6. Tools and Resources for Chord Identification
Here are some useful tools and resources to aid your chord identification journey:
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Online Chord Finders | Websites that identify chords based on notes entered. |
| Ear Training Apps | Apps that help you develop your ear to recognize intervals and chords. |
| Music Theory Books | Books that provide comprehensive knowledge of music theory concepts. |
| Guitar Chord Dictionaries | Books or websites with extensive lists of guitar chord diagrams. |
| Online Guitar Communities | Forums and groups where you can discuss chord identification with other guitarists, like guitarplayers.net. |
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Relying Too Heavily on Chord Charts: While chord charts can be helpful, relying too much on them can hinder your ability to identify chords by ear.
- Ignoring the Context of the Song: Always consider the context of the song when trying to identify chords. The key signature, melody, and chord progression can all provide valuable clues.
- Not Practicing Regularly: Like any skill, chord identification requires regular practice. Set aside time each day to practice your ear training and chord analysis skills.
- Getting Discouraged Easily: Chord identification can be challenging, especially in the beginning. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t get it right away. Keep practicing and you will eventually improve.
- Neglecting Music Theory: A strong understanding of music theory is essential for chord identification. Don’t neglect your music theory studies.
8. The Benefits of Mastering Chord Identification
Mastering chord identification unlocks a world of possibilities for guitarists.
- Improved Ear Training: Develop a keen sense of pitch and harmony.
- Enhanced Improvisation Skills: Play more confidently and creatively.
- Deeper Understanding of Music: Appreciate the intricacies of musical composition.
- Increased Songwriting Abilities: Create your own original music with greater ease.
- Better Communication with Other Musicians: Talk about music with precision.
According to Guitar Player Magazine, mastering chord identification empowers guitarists to become more versatile and expressive musicians.
9. Real-World Applications
The ability to identify chords has many practical applications for guitarists.
- Learning Songs Quickly: Figure out the chords to your favorite songs by ear.
- Jamming with Other Musicians: Play along with other musicians in any key.
- Transcribing Music: Accurately write down the chords to any song.
- Teaching Guitar: Help your students learn to identify chords.
- Working as a Session Musician: Quickly learn chord charts in recording sessions.
10. Level Up Your Guitar Skills with GuitarPlayers.net
Ready to take your guitar playing to the next level? Visit guitarplayers.net for a wealth of resources, including:
- Extensive lesson library: From beginner basics to advanced techniques.
- Comprehensive guitar and gear reviews: Make informed purchasing decisions.
- Vast collection of sheet music: Play your favorite songs and discover new ones.
- Active community forum: Connect with fellow guitar enthusiasts, share tips, and ask questions.
Whether you’re a beginner just starting out or an experienced player looking to hone your skills, guitarplayers.net has everything you need to achieve your musical goals. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to join a thriving community of guitar lovers and unlock your full potential.
Address: 1140 Boylston Street, Boston, MA 02215, United States.
Phone: +1 (617) 747-2261.
Website: guitarplayers.net.
What are you waiting for? Explore guitarplayers.net today and embark on a rewarding musical journey!
FAQ: Chord Identification on Guitar
1. What is a chord in guitar terms?
A chord on guitar is a combination of three or more notes played simultaneously, creating harmony. These notes are usually related, forming a specific musical quality like major, minor, or dominant. Understanding how these notes interact is key to identifying chords.
2. How do I find the root note of a chord on guitar?
To find the root note, look for the lowest note in the chord voicing, especially in power chords where it’s the only bass note. Chord diagrams often highlight the root, and listening for the emphasized note in the bassline can also guide you.
3. What are the most common guitar chord qualities?
The most common guitar chord qualities include major (happy, bright), minor (sad, melancholic), dominant 7th (complex, bluesy), diminished (tense), and augmented (dissonant). Each has a distinct sound due to its unique interval structure.
4. Why is it harder to identify chords on guitar than on piano?
It’s harder to identify chords on guitar because the same note can be played in multiple positions, making it challenging to visualize intervals. The fretboard layout complicates recognizing the root and chord structure compared to the linear arrangement of piano keys.
5. How does understanding music theory help in chord identification?
Understanding music theory helps by providing a framework for chord construction, intervals, and relationships to scales. This knowledge enables you to analyze chords based on their components rather than relying solely on memorization.
6. Can ear training really improve my chord identification skills?
Yes, ear training significantly improves chord identification by developing your ability to recognize intervals and chord qualities by ear. Regular practice hones your auditory skills, making it easier to identify chords without visual aids.
7. What are some online tools for identifying guitar chords?
Some popular online tools for identifying guitar chords include chord namers like jguitar.com/chordname, which allow you to input notes and receive chord suggestions. These are helpful for quick reference and learning new voicings.
8. How do chord progressions assist in identifying chords?
Chord progressions provide context, as chords often follow predictable patterns. Recognizing common progressions (like I-IV-V) helps anticipate chord changes and quickly identify chords based on their function within the sequence.
9. What is a slash chord, and how do I identify it?
A slash chord is a chord with a non-root bass note (e.g., C/G). Identify it by recognizing the primary chord (C) and noting the bass note (G). Slash chords create smooth transitions and add harmonic interest.
10. How can guitarplayers.net help me improve my chord identification skills?
guitarplayers.net offers lessons, reviews, sheet music, and a community forum to enhance your skills. The lessons cover music theory and chord voicings, the sheet music provides real-world examples, and the community allows you to discuss and learn from other guitarists.

