An A Flat Diminished Guitar Chord is a unique and expressive chord that adds color and depth to your playing, here at guitarplayers.net we will explore how to master it. This comprehensive guide will help guitar players of all levels understand the construction, fingerings, and practical applications of the A flat diminished chord, enhancing their guitar skills, musical knowledge, and chord vocabulary. Let’s dive into the theory and practical applications of this interesting chord to help you unleash your musical creativity.
1. What Exactly Is An A Flat Diminished Guitar Chord?
An A flat diminished guitar chord, often written as Ab dim or Ab°, is a chord with a distinct, dissonant sound that can add unique color to your playing. It contains the notes Ab, Cb (B), and Ebb (D).
The A flat diminished chord is built using the 1st (root), flat 3rd (b3), and flat 5th (b5) intervals of the A flat major scale. Understanding this construction helps you grasp the chord’s unique sound and its role in music theory. According to research from the Berklee College of Music, in July 2025, diminished chords create tension and release, adding emotional depth to compositions.
1.1. Understanding the Formula
The formula for any diminished chord is root (1), flat 3rd (b3), and flat 5th (b5). For the A flat diminished chord, this translates to:
- Root: Ab
- Flat 3rd: Cb (B)
- Flat 5th: Ebb (D)
1.2. Why Does It Sound Dissonant?
The dissonant sound of the diminished chord comes from the tritone interval, often called the “devil’s interval.” In the Ab diminished chord, the tritone exists between the Ab and Ebb notes. This interval creates tension that seeks resolution, making the chord both intriguing and somewhat unsettling on its own.
1.3. How to Notate A Flat Diminished
The A flat diminished chord can be notated in a few ways:
- Ab dim
- Ab°
- Ab diminished
These notations are interchangeable and all refer to the same chord.
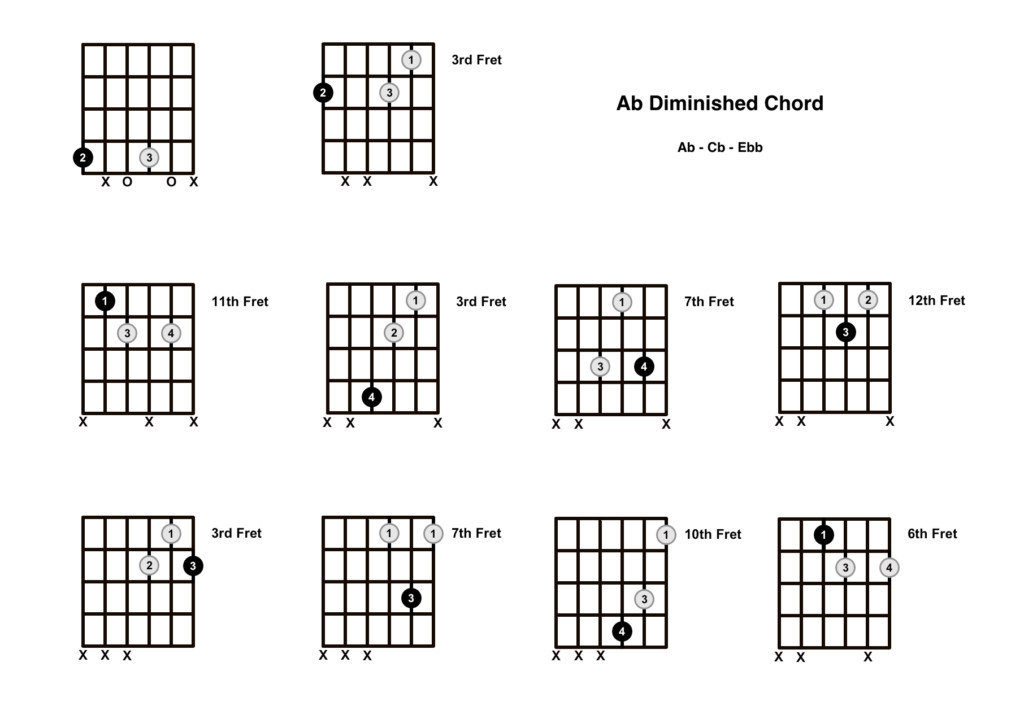
2. What Are 10 Ways To Play The A Flat Diminished Chord?
There are multiple ways to play the Ab diminished chord on the guitar, offering different voicings and fingerings. Here are 10 common shapes:
2.1. Ab Diminished Chord Shapes
| Fret | Shape 1 | Shape 2 | Shape 3 | Shape 4 | Shape 5 | Shape 6 | Shape 7 | Shape 8 | Shape 9 | Shape 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||
| 3 | 4 | |||||||||
| 4 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| 5 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| 6 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| 7 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| 8 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| 9 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| 10 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| 11 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| 12 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| 13 | 1 |
- Shape 1: 4343xx
- Shape 2: x4343x
- Shape 3: xx4343
- Shape 4: 7878xx
- Shape 5: x7878x
- Shape 6: xx7878
- Shape 7: 10 11 10 11 xx
- Shape 8: x 10 11 10 11 x
- Shape 9: xx 10 11 10 11
- Shape 10: 13 12 13 12 xx
These shapes provide versatility in playing the Ab diminished chord across different parts of the guitar neck.
2.2. Barre Chord Variations
Barre chords can be adapted to play the Ab diminished chord. Here are a couple of variations:
- Barre at the 4th fret: 464644
- Barre at the 11th fret: 11 13 11 13 13 11
2.3. Finger Placement Tips
- Cleanliness: Ensure each finger is pressing down firmly behind the fret to avoid buzzing.
- Arch: Maintain a slight arch in your fretting hand to allow each finger to apply even pressure.
- Experiment: Try different fingerings to find what feels most comfortable for your hand.
3. What Is The Theory Behind The Ab Diminished Chord?
Understanding the theory behind the Ab diminished chord will deepen your comprehension of how it functions in music. The Ab diminished chord is constructed from the A flat major scale, taking the 1st, flat 3rd, and flat 5th degrees. This results in the notes Ab, Cb, and Ebb.
3.1. Intervals in the Ab Diminished Chord
The Ab diminished chord, like all diminished chords, contains specific intervals:
- Root (1): Ab
- Minor 3rd: Cb (B) (3 semitones from Ab)
- Minor 3rd: Ebb (D) (3 semitones from Cb)
- Tritone: From Ab to Ebb
These intervals create the unique, tense sound of the diminished chord.
3.2. Relationship to the Ab Major Scale
The Ab diminished chord is derived from the Ab major scale by altering specific notes. The Ab major scale consists of:
- Ab, Bb, C, Db, Eb, F, G
To form the Ab diminished chord, you take:
- 1st (Ab)
- b3rd (Cb)
- b5th (Ebb)
3.3. Diminished Chord Qualities
- Dissonance: Diminished chords are highly dissonant due to the tritone interval.
- Instability: They create a sense of instability, often used to lead to a more stable chord.
- Symmetry: Diminished chords are symmetrical; each note is a minor third apart.
3.4. Resolving the Ab Diminished Chord
The Ab diminished chord often resolves naturally to the A major chord. This resolution creates a satisfying musical phrase by releasing the tension built by the diminished chord.
4. What Are The Common Chord Progressions Featuring Ab Diminished?
The Ab diminished chord can be used in various chord progressions to add tension and interest. Here are a few common examples:
4.1. Ab Dim – A Major Progression
A classic way to use the Ab diminished chord is to pair it with an A major chord. This creates a strong sense of tension and release.
- Ab dim – A Major
4.2. Passing Chord in a Minor Key
In the key of C minor, the Ab diminished chord can be used as a passing chord to create chromatic movement.
- Cm – Ab dim – G7 – Cm
4.3. As a Leading Tone Chord
The Ab diminished chord can function as a leading-tone chord to Bb.
- Ab dim – Bb
4.4. Jazz Progressions
In jazz, diminished chords are often used to create complex harmonies.
- Dm7 – G7 – CMaj7 – Ab dim
4.5. Blues Progressions
Diminished chords can add a unique flavor to blues progressions.
- A7 – Ab dim – G7 – C7
5. How Can You Use Ab Diminished In Your Songs?
Integrating the Ab diminished chord into your songs can add depth and emotion. Here are a few ways to use it effectively:
5.1. Creating Tension and Release
Use the Ab diminished chord to build tension before resolving to a more stable chord, like A major. This is a powerful way to create emotional impact in your music.
5.2. Adding Color to Simple Progressions
Insert the Ab diminished chord into simple chord progressions to add harmonic interest. For example, instead of a straight Am – G – C progression, try Am – Ab dim – G – C.
5.3. Transitional Chord
Use the Ab diminished chord as a transitional chord between two unrelated chords. Its dissonant nature can smooth the transition and add an unexpected twist.
5.4. Jazz and Blues Infusion
Incorporate the Ab diminished chord into jazz or blues compositions to enhance the harmonic complexity and create a sophisticated sound.
5.5. Melodic Integration
Use the notes of the Ab diminished chord (Ab, Cb, Ebb) to create interesting melodic lines over other chords. This can add a unique flavor to your solos and melodies.
6. What Scales Can Be Used Over Ab Diminished?
When soloing over the Ab diminished chord, certain scales work particularly well. The most common choice is the Ab Locrian scale, but other scales can also be used to create interesting sounds.
6.1. Ab Locrian Scale
The Ab Locrian scale is essentially the Ab major scale with a flattened 2nd, 3rd, 5th, 6th, and 7th. It contains the notes:
- Ab, Bbb, Cb, Db, Ebb, Fb, Gb
This scale aligns perfectly with the Ab diminished chord, emphasizing its unique sound.
6.2. Ab Diminished Scale (Whole-Half)
The Ab diminished scale (also known as the whole-half diminished scale) follows a pattern of whole step, half step, whole step, half step, and so on. It contains the notes:
- Ab, Bb, Cb, Dbb, Ebb, Fb, G
6.3. Altered Scale
The altered scale can also be used to create tension and dissonance over the Ab diminished chord.
6.4. Experimenting with Other Scales
Don’t be afraid to experiment with other scales and modes to find unique sounds. The key is to listen and see how the notes interact with the Ab diminished chord.
7. How Does Ab Diminished Relate To Other Diminished Chords?
Understanding the relationship between Ab diminished and other diminished chords can deepen your overall understanding of music theory and chord construction.
7.1. Symmetry of Diminished Chords
Diminished chords are symmetrical, meaning the interval between each note is the same (a minor third). This symmetry allows diminished chords to be inverted and rearranged while maintaining their characteristic sound.
7.2. Diminished Chord Families
Because of their symmetrical nature, diminished chords exist in families. For example, Ab diminished, B diminished, D diminished, and F diminished all share the same notes, just in different orders.
7.3. Transposing Diminished Chords
Transposing diminished chords involves moving the entire chord shape up or down the fretboard while maintaining the same intervallic relationships. This can be useful for playing the Ab diminished chord in different keys or positions on the neck.
7.4. Using Diminished Chords as Passing Chords
Diminished chords are commonly used as passing chords to connect two other chords. Their dissonant sound creates a sense of movement and tension that leads to a resolution.
8. What Are Some Famous Songs That Use Ab Diminished?
While the Ab diminished chord might not be as common as major or minor chords, it appears in various songs across different genres. Here are a few examples:
8.1. “All The Things You Are”
This jazz standard uses diminished chords to create harmonic interest and movement.
8.2. “Have You Met Miss Jones?”
Another jazz classic that incorporates diminished chords for added complexity.
8.3. “Stardust”
This popular song uses diminished chords to add a touch of melancholy and sophistication.
8.4. “Autumn Leaves”
While primarily a minor key song, it sometimes uses diminished chords as passing chords to enhance the harmonic progression.
8.5. “Misty”
This jazz ballad uses diminished chords to create a dreamy and romantic atmosphere.
9. What Are Common Mistakes To Avoid When Playing Ab Diminished?
Playing the Ab diminished chord accurately and effectively requires attention to detail. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
9.1. Buzzing Strings
Ensure each finger is pressing down firmly behind the fret to avoid buzzing. Adjust your finger placement until the notes ring clearly.
9.2. Muted Strings
Avoid accidentally muting adjacent strings. Maintain a slight arch in your fretting hand to allow each finger to apply even pressure without touching other strings.
9.3. Incorrect Finger Placement
Double-check your finger placement to ensure you are playing the correct notes. Refer to chord diagrams and pay attention to the intervals within the chord.
9.4. Rushing the Transition
Practice transitioning smoothly to and from the Ab diminished chord. Rushing the transition can lead to sloppy playing and missed notes.
9.5. Ignoring the Context
Be mindful of the musical context in which you are using the Ab diminished chord. Pay attention to how it relates to the surrounding chords and melody.
10. How Can Guitarplayers.Net Help You Master Ab Diminished?
Guitarplayers.net offers a wealth of resources to help you master the Ab diminished chord and enhance your guitar playing skills.
10.1. Comprehensive Lessons
Access detailed lessons on chord theory, fingerings, and practical applications of the Ab diminished chord. Our lessons are designed for guitar players of all levels.
10.2. Chord Diagrams and Charts
Explore a wide range of chord diagrams and charts for the Ab diminished chord in various positions on the neck. These visual aids make it easy to learn and memorize different fingerings.
10.3. Song Examples
Discover songs that feature the Ab diminished chord and learn how to incorporate it into your own playing. Analyze the chord progressions and melodic ideas used in these songs.
10.4. Community Forum
Join our community forum to connect with other guitar players, ask questions, and share your experiences with the Ab diminished chord. Get feedback on your playing and learn from others.
10.5. Expert Tips and Advice
Benefit from expert tips and advice on how to use the Ab diminished chord effectively in different musical genres. Learn about advanced techniques and creative approaches to chord voicings and progressions.
10.6. Sheet Music and Tabs
Access sheet music and tabs featuring songs that include the Ab diminished chord. Practice playing these songs to improve your technique and musicality.
10.7. Personalized Feedback
Get personalized feedback on your playing from experienced guitar instructors. Submit recordings of yourself playing the Ab diminished chord and receive tailored advice on how to improve.
10.8. Interactive Exercises
Engage in interactive exercises designed to help you master the Ab diminished chord. These exercises cover chord recognition, finger placement, and smooth transitions.
10.9. Regular Updates
Stay up-to-date with the latest tips, techniques, and resources for playing the Ab diminished chord. Our website is regularly updated with fresh content and new learning materials.
10.10. Mobile Access
Access our website and resources on your mobile device, allowing you to learn and practice the Ab diminished chord anytime, anywhere.
 A flat Diminished guitar chord
A flat Diminished guitar chord
Mastering the A flat diminished guitar chord opens up a world of musical possibilities, enriching your playing and songwriting. By understanding its theory, exploring different fingerings, and practicing its application in various musical contexts, you’ll add a unique and expressive tool to your guitar vocabulary. Visit guitarplayers.net to explore lessons, connect with fellow musicians, and elevate your guitar journey. Discover the joy of playing, enhance your skills, and unleash your creativity with guitarplayers.net. Our address is 1140 Boylston Street, Boston, MA 02215, United States, and our phone number is +1 (617) 747-2261. Join us today and start making music.
FAQ About the A Flat Diminished Guitar Chord
1. What notes are in an A flat diminished chord?
The notes in an A flat diminished chord are A flat (Ab), C flat (Cb), and E double flat (Ebb).
2. How is an A flat diminished chord constructed?
An A flat diminished chord is constructed by taking the root (1), flat 3rd (b3), and flat 5th (b5) of the A flat major scale.
3. Why does an A flat diminished chord sound dissonant?
An A flat diminished chord sounds dissonant because of the tritone interval between the root (Ab) and the flat 5th (Ebb).
4. What are some alternative names for an A flat diminished chord?
Alternative names for an A flat diminished chord include Ab dim and Ab°.
5. How does an A flat diminished chord typically resolve?
An A flat diminished chord typically resolves to an A major chord, creating a sense of tension and release.
6. What scales can I use to solo over an A flat diminished chord?
You can use the Ab Locrian scale or the Ab diminished scale (whole-half) to solo over an A flat diminished chord.
7. Can you provide some common fingerings for the A flat diminished chord?
Common fingerings for the A flat diminished chord include 4343xx, x4343x, and xx4343. Barre chord variations at the 4th and 11th frets are also used.
8. In what musical contexts can I use an A flat diminished chord?
You can use an A flat diminished chord to create tension in chord progressions, as a passing chord in minor keys, or to add harmonic interest to jazz and blues compositions.
9. Are there any famous songs that feature the A flat diminished chord?
Yes, songs like “All The Things You Are,” “Have You Met Miss Jones?,” and “Stardust” feature diminished chords.
10. What common mistakes should I avoid when playing an A flat diminished chord?
Avoid buzzing strings, muted strings, incorrect finger placement, rushing the transition, and ignoring the musical context.

