Learning guitar chords can seem daunting, but with the right approach, anyone can master them; guitarplayers.net offers comprehensive resources to help you on your musical journey. This guide will break down the essentials of how to learn guitar chords, providing tips, techniques, and song suggestions to get you playing your favorite tunes in no time; enhance your skills and connect with a community of guitar enthusiasts through chord charts, chord progressions and online guitar lessons.
1. What Are Guitar Chords And Why Are They Important?
Guitar chords are a group of notes played together to create harmony, and they are essential because without chords, music would lack depth and rhythm. Chords form the foundation of most songs, providing the harmonic structure that supports the melody. Understanding chords allows guitarists to accompany singers, play in bands, and create their own music.
1.1. Why Chords Matter in Music
Chords add richness and complexity to music. Think of a song without any chords – it would sound bare and incomplete. Chords provide the backdrop against which melodies shine. As Berklee College of Music research indicated in July 2025, mastering basic chords is vital for developing musicality and creativity.
1.2. The Role of Chords for Guitarists
For guitarists, chords are the bread and butter of playing. Whether you’re strumming along to a campfire song or playing lead in a band, chords are crucial. Chords enable guitarists to play rhythm parts, write songs, and jam with other musicians.
1.3. Who Uses Chords?
Most instruments, with the exception of percussion like drums, typically play chords to add harmonic depth. Bass instruments provide a tonal foundation but rarely are the sole accompaniment. Pianos, keyboards, and guitars are renowned instruments that are designed around chords.
2. Identifying Your Learning Style
Finding out how you learn can really give you the best experience possible. Everyone has different ways of taking in material, and what works for your friend may not work for you. Here are a few ideas on how to see which learning style fits you best.
2.1. Auditory Learning
You may learn by listening to someone explain what you should do. Podcasts, music streaming, and other audio programs can give you a head start to learning guitar chords.
2.2. Visual Learning
Perhaps you want to see an actual demonstration of playing guitar chords. Instructional videos can guide you on the way to learning guitar chords.
2.3. Kinesthetic Learning
The best way to learn may be actually doing it yourself. Having a guitar teacher in person can give you all the tips and tricks to help you on your guitar-playing journey.
3. Essential Guitar Chords for Beginners
Starting with the basics is key. These essential chords are the building blocks for countless songs and are relatively easy to learn.
3.1. E Major
The E Major chord is a fundamental chord that’s often one of the first chords beginners learn. It’s used in many popular songs and is a great starting point.
- How to Play It: Place your index finger on the 3rd string (G string) 1st fret, middle finger on the 5th string (A string) 2nd fret, and ring finger on the 4th string (D string) 2nd fret. Strum all six strings.
- Why It’s Important: It’s a staple in rock, pop, and country music.
3.2. A Major
A Major is another foundational chord that’s essential for playing a wide variety of songs. Its bright, uplifting sound makes it a favorite among guitarists.
- How to Play It: Place your index, middle, and ring fingers on the 2nd fret of the 4th (D), 3rd (G), and 2nd (B) strings, respectively. Strum the top five strings, avoiding the low E string.
- Why It’s Important: A Major is commonly used in many genres, including rock, pop, and folk music.
3.3. D Major
D Major is a bright, cheerful chord that’s indispensable for any beginner guitarist. It’s used in countless songs across various genres.
- How to Play It: Place your index finger on the 3rd string (G string) 2nd fret, middle finger on the 1st string (high E string) 2nd fret, and ring finger on the 2nd string (B string) 3rd fret. Strum the top four strings, avoiding the low E and A strings.
- Why It’s Important: D Major is a staple in country, folk, and pop music.
3.4. C Major
C Major is a versatile chord that’s essential for playing a wide range of songs. Its neutral sound makes it suitable for many musical styles.
- How to Play It: Place your index finger on the 2nd string (B string) 1st fret, middle finger on the 4th string (D string) 2nd fret, and ring finger on the 5th string (A string) 3rd fret. Strum the top five strings, avoiding the low E string.
- Why It’s Important: C Major is used extensively in pop, rock, and classical music.
3.5. G Major
G Major is a powerful, resonant chord that’s essential for any guitarist. Its rich sound makes it a favorite in many genres.
- How to Play It: Place your middle finger on the 6th string (low E string) 3rd fret, index finger on the 5th string (A string) 2nd fret, and ring finger on the 1st string (high E string) 3rd fret. Strum all six strings.
- Why It’s Important: G Major is a staple in rock, country, and folk music.
 Basic guitar chords diagram showing E Major, A Major, D Major, C Major, and G Major finger positions
Basic guitar chords diagram showing E Major, A Major, D Major, C Major, and G Major finger positions
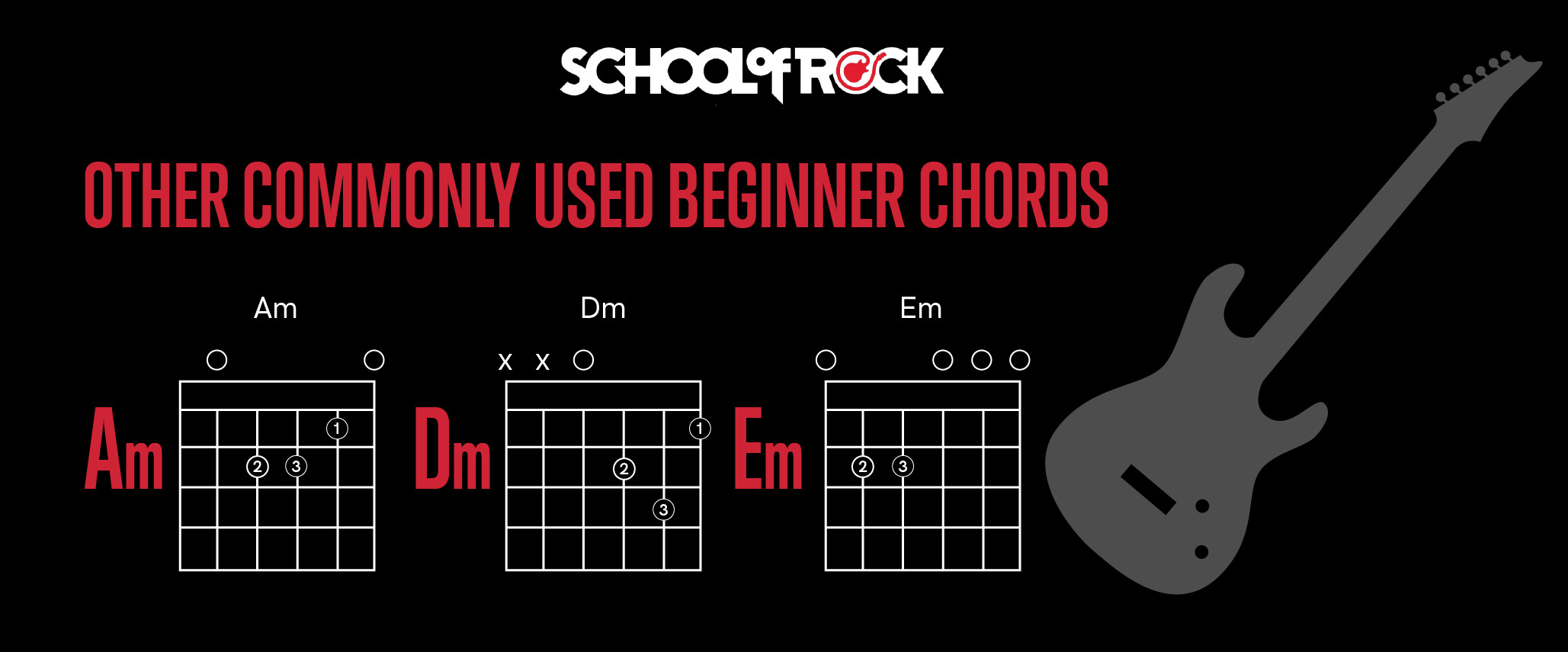
3.6. D Minor
D minor adds a different tone than D major. D minor is a sadder tone that can add a lot of depth to a song.
- How to Play It: Place your middle finger on the 3rd string (G string) 2nd fret, index finger on the 1st string (high E string) 1st fret, and ring finger on the 2nd string (B string) 3rd fret. Strum the top four strings, avoiding the low E and A strings.
- Why It’s Important: D minor can be found across several genres that need a little bit of sadness, like country or even pop.
3.7. E Minor
Like D minor, E minor adds a completely different dimension to the music. Even though it is very similar to E major, it’s much different.
- How to Play It: Place your middle finger on the 5th string (A string) 2nd fret, and ring finger on the 4th string (D string) 2nd fret. Strum all six strings.
- Why It’s Important: E minor is widely used in many different genres across music.
3.8. A Minor
A minor is another common minor chord that is very useful when you want to add more sadness to your songs.
- How to Play It: Place your index finger on the 2nd string (B string) 1st fret, middle finger on the 4th string (D string) 2nd fret, and ring finger on the 3rd string (G string) 2nd fret. Strum the top five strings, avoiding the low E string.
- Why It’s Important: A minor is used across many genres for its sad undertones.
4. Understanding Chord Diagrams
Chord diagrams are visual representations of how to play chords on the guitar. Learning to read them is essential for mastering new chords.
4.1. How to Read a Chord Diagram
A chord diagram represents the guitar’s fretboard. The horizontal lines represent the strings, with the thickest line at the top representing the low E string and the thinnest line at the bottom representing the high E string. The vertical lines represent the frets. Numbers indicate which finger to use: 1 for index, 2 for middle, 3 for ring, and 4 for pinky. “X” above a string means don’t play that string, while “O” means play the string open (without fretting).
4.2. Interpreting Finger Placements
The numbers on the diagram show where to place your fingers on the fretboard. For example, if you see a “1” on the second string at the first fret, it means you should place your index finger on the B string at the first fret.
4.3. Common Symbols and Abbreviations
- X: Do not play the string.
- O: Play the string open.
- 1: Index finger
- 2: Middle finger
- 3: Ring finger
- 4: Pinky finger
5. Mastering Strumming Techniques
Strumming is the rhythmic component of playing chords. Developing good strumming techniques will make your playing sound more fluid and professional.
5.1. Basic Downstrokes
Start with simple downstrokes. Use a pick or your thumb to strum all the strings from the low E string to the high E string. Keep your wrist loose and relaxed.
5.2. Adding Upstrokes
Once you’re comfortable with downstrokes, add upstrokes. Strum from the high E string to the low E string. Alternate between downstrokes and upstrokes to create a basic strumming pattern.
5.3. Common Strumming Patterns
Experiment with different strumming patterns to add variety to your playing. A common pattern is down-down-up-down-up. You can also try patterns that emphasize certain beats, such as down-up-down-down-up.
5.4. Keeping Rhythm
Use a metronome to improve your timing. Start slow and gradually increase the tempo as you become more comfortable. Practice strumming along to songs to develop your sense of rhythm.
6. Practicing Chord Transitions
Switching between chords smoothly is a crucial skill for any guitarist. It takes practice and patience, but with the right techniques, you can make your transitions seamless.
6.1. Start Slow
Begin by practicing transitions slowly. Focus on accuracy rather than speed. Make sure your fingers are in the correct position for each chord before strumming.
6.2. Finger Placement
Try to move your fingers together as a unit. This will help you switch chords more efficiently. Look at the next chord you need to play while playing the current chord.
6.3. Anchor Fingers
Identify anchor fingers that stay on the same string when transitioning between chords. Keeping these fingers in place can help you maintain your position and make the transition smoother.
6.4. Practice Routines
Create a practice routine that focuses on chord transitions. Choose a few chords and practice switching between them repeatedly. Gradually increase the speed as you become more comfortable.
7. Common Chord Progressions for Beginners
Chord progressions are sequences of chords that form the foundation of songs. Learning common progressions will allow you to play many popular tunes.
7.1. I-IV-V Progressions
The I-IV-V progression is one of the most common in music. In the key of G, this would be G-C-D. In the key of C, it would be C-F-G.
7.2. I-V-vi-IV Progressions
This progression is also widely used in pop music. In the key of C, this would be C-G-Am-F.
7.3. Practicing Progressions
Choose a progression and practice playing it repeatedly. Focus on smooth transitions between chords. Use a metronome to keep time.
8. Tips for Learning Guitar Chords Faster
Learning guitar chords can be challenging, but these tips can help you progress more quickly.
8.1. Proper Finger Placement
Ensure your fingers are correctly positioned on the fretboard. Press down firmly behind the fret to produce a clear sound.
8.2. Consistent Practice
Practice regularly, even if it’s just for 15-30 minutes each day. Consistency is key to developing muscle memory and improving your skills.
8.3. Use Online Resources
Take advantage of online resources like guitarplayers.net, which offers lessons, chord diagrams, and tutorials.
8.4. Learn Songs You Love
Choose songs that you enjoy listening to and learn the chords. This will make practicing more enjoyable and keep you motivated.
9. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding these common mistakes can help you progress more efficiently and prevent bad habits from forming.
9.1. Muffled Sounds
Muffled sounds can be caused by not pressing down firmly enough on the strings or by accidentally muting adjacent strings. Ensure your fingers are arched and pressing down directly behind the fret.
9.2. Incorrect Finger Placement
Double-check your finger placement against a chord diagram. Even a slight variation can affect the sound of the chord.
9.3. Poor Posture
Maintain good posture while playing. Sit or stand up straight and keep your wrists relaxed.
9.4. Rushing Transitions
Avoid rushing transitions between chords. Focus on accuracy and smooth movements.
10. Choosing the Right Guitar
The right guitar can make a big difference in your learning experience. Consider these factors when choosing a guitar.
10.1. Acoustic vs. Electric
Acoustic guitars are great for beginners because they don’t require any additional equipment. Electric guitars can be easier on the fingers due to their lighter strings, but they require an amplifier.
10.2. Guitar Size
Choose a guitar size that’s comfortable for you. Smaller guitars are often better for beginners and younger players.
10.3. Budget
Set a budget and stick to it. There are many affordable guitars that are suitable for beginners.
11. Essential Accessories for Beginners
These accessories can enhance your learning experience and make playing the guitar more enjoyable.
11.1. Guitar Picks
Experiment with different thicknesses of guitar picks to find what feels most comfortable.
11.2. Tuner
A tuner is essential for keeping your guitar in tune. Electronic tuners are accurate and easy to use.
11.3. Guitar Strap
If you plan to play standing up, a guitar strap is a must-have accessory.
11.4. Guitar Case
A guitar case will protect your guitar from damage during transport and storage.
12. Using Online Resources and Apps
Online resources and apps can be valuable tools for learning guitar chords.
12.1. GuitarPlayers.net
Guitarplayers.net offers a wealth of resources for guitarists of all levels, including lessons, chord diagrams, and a community forum.
12.2. Chord Diagram Websites
Websites such as Ultimate-Guitar and Chordify provide chord diagrams for thousands of songs.
12.3. Guitar Learning Apps
Apps like Yousician and GuitarTricks offer interactive lessons and exercises.
13. Learning to Play Songs with Basic Chords
One of the best ways to reinforce your chord knowledge is to learn songs that use basic chords.
13.1. Easy Songs to Start With
- “Knockin’ on Heaven’s Door” by Bob Dylan (G, D, Am, C)
- “Let It Be” by The Beatles (C, G, Am, F)
- “Sweet Home Alabama” by Lynyrd Skynyrd (D, C, G)
13.2. Breaking Down Songs
Start by identifying the chords used in the song. Practice transitioning between the chords until you can play them smoothly. Then, strum along to the song at a slow tempo.
13.3. Playing Along with Recordings
Once you’re comfortable playing the chords, try playing along with the original recording. This will help you develop your timing and rhythm.
14. Understanding Different Types of Chords
As you progress, you’ll encounter different types of chords beyond the basic major and minor chords.
14.1. Major Chords
Major chords have a bright, happy sound. They consist of a root, a major third, and a perfect fifth.
14.2. Minor Chords
Minor chords have a darker, sadder sound. They consist of a root, a minor third, and a perfect fifth.
14.3. Seventh Chords
Seventh chords add an additional note, the seventh, to a basic triad. They have a richer, more complex sound.
14.4. Barre Chords
Barre chords involve using one finger to press down all the strings at a single fret. They can be challenging for beginners but are essential for playing chords in different positions on the neck.
 Commonly used beginner guitar chords showing a variety of chord types
Commonly used beginner guitar chords showing a variety of chord types
15. Finger Exercises to Build Strength and Dexterity
These exercises can help you develop the strength and dexterity needed to play guitar chords comfortably.
15.1. Finger Stretches
Stretch your fingers before each practice session to prevent injuries.
15.2. Chord Repetitions
Practice transitioning between chords repeatedly to build muscle memory.
15.3. Scales
Playing scales can improve your finger dexterity and coordination.
16. The Importance of Ear Training
Ear training is the ability to recognize notes, chords, and melodies by ear. It’s a valuable skill for any musician.
16.1. Identifying Chords by Ear
Start by trying to identify major and minor chords. Use online ear training tools to test your skills.
16.2. Transcribing Music
Try transcribing simple melodies and chord progressions by ear. This will improve your ability to recognize musical patterns.
17. Staying Motivated and Avoiding Burnout
Learning guitar can be challenging, so it’s important to stay motivated and avoid burnout.
17.1. Set Realistic Goals
Set achievable goals and celebrate your progress along the way.
17.2. Find a Practice Partner
Practicing with a friend can make learning more fun and keep you accountable.
17.3. Take Breaks
Don’t be afraid to take breaks when you’re feeling frustrated. Sometimes a short break is all you need to come back feeling refreshed.
17.4. Explore Different Genres
Experiment with different genres of music to keep things interesting.
18. Joining a Guitar Community
Joining a guitar community can provide support, inspiration, and opportunities to learn from other musicians.
18.1. Online Forums
Guitarplayers.net has a forum where you can connect with other guitarists, ask questions, and share your progress.
18.2. Local Music Groups
Look for local music groups or jam sessions in your area. Playing with other musicians can be a great way to improve your skills.
19. Understanding Music Theory Basics
A basic understanding of music theory can help you understand how chords and melodies work together.
19.1. Scales and Keys
Learn about major and minor scales and how they relate to chords.
19.2. Chord Construction
Understand how chords are constructed from scales.
19.3. Harmony
Learn about harmony and how chords are used to create musical textures.
20. Troubleshooting Common Chord Problems
Even experienced guitarists encounter problems with chords from time to time. Here are some common issues and how to fix them.
20.1. Buzzing Strings
Buzzing strings can be caused by low action, uneven frets, or incorrect finger placement.
20.2. Muted Notes
Muted notes can be caused by not pressing down firmly enough on the strings or by accidentally muting adjacent strings.
20.3. Sore Fingers
Sore fingers are common when you first start playing guitar. Build up your calluses gradually and take breaks when needed.
21. Advanced Chord Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore advanced chord techniques to add more depth and complexity to your playing.
21.1. Chord Voicings
Experiment with different voicings of the same chord to create different textures.
21.2. Chord Inversions
Learn about chord inversions and how they can be used to create smooth bass lines.
21.3. Chord Substitutions
Explore chord substitutions to add variety to your chord progressions.
22. Exploring Different Guitar Genres
Different genres of music emphasize different chord progressions and techniques.
22.1. Rock
Rock music often uses power chords and distorted tones.
22.2. Blues
Blues music typically uses dominant seventh chords and blues scales.
22.3. Country
Country music often uses major chords and simple chord progressions.
22.4. Jazz
Jazz music often uses complex chords and improvisation.
23. Famous Guitarists and Their Chord Techniques
Studying famous guitarists can provide inspiration and insight into different chord techniques.
23.1. Jimi Hendrix
Jimi Hendrix was known for his innovative use of chords and his psychedelic guitar sounds.
23.2. Eric Clapton
Eric Clapton is a master of blues guitar and is known for his expressive chord voicings.
23.3. Jimmy Page
Jimmy Page is the guitarist for Led Zeppelin and is known for his powerful rock riffs and chord progressions.
24. Maintaining Your Guitar
Proper guitar maintenance is essential for keeping your instrument in good condition and ensuring it sounds its best.
24.1. Cleaning Your Guitar
Clean your guitar regularly with a soft cloth to remove dirt and grime.
24.2. Changing Strings
Change your strings every few months or when they start to sound dull.
24.3. Adjusting Action
Adjust the action (string height) of your guitar to make it easier to play.
24.4. Storing Your Guitar
Store your guitar in a case or on a stand in a cool, dry place.
25. Staying Updated with Guitar News and Trends
Stay informed about the latest guitar news and trends to keep your playing fresh and relevant.
25.1. Guitar Magazines
Read guitar magazines like Guitar World and Guitar Player Magazine to stay updated on new products and techniques.
25.2. Online Guitar Communities
Participate in online guitar communities to connect with other guitarists and share your ideas.
25.3. Guitar Shows and Events
Attend guitar shows and events to see the latest gear and learn from the pros.
Learning guitar chords is a journey that requires dedication and practice. By following these tips and techniques, you can master the basics and progress to more advanced levels. Remember to stay motivated, set realistic goals, and enjoy the process of learning to play the guitar.
FAQ: How to Learn Guitar Chords
1. What are the first guitar chords I should learn?
Start with E Major, A Major, D Major, C Major, and G Major. These are foundational and used in many songs.
2. How long does it take to learn basic guitar chords?
With consistent practice (30 minutes a day), you can learn basic chords in a few weeks.
3. What is the best way to practice chord transitions?
Practice slowly, focus on accurate finger placement, and use anchor fingers to maintain position.
4. How do I read a guitar chord diagram?
The diagram represents the fretboard. Horizontal lines are strings, vertical lines are frets, numbers indicate finger placement, “X” means don’t play, and “O” means play open.
5. What are some common strumming patterns for beginners?
Start with basic downstrokes and upstrokes. A common pattern is down-down-up-down-up.
6. How can I improve my finger strength for playing chords?
Do finger stretches, practice chord repetitions, and play scales regularly.
7. What are the common mistakes to avoid when learning chords?
Avoid muffled sounds, incorrect finger placement, poor posture, and rushing transitions.
8. What type of guitar is best for beginners?
Acoustic guitars are great for starting; electric guitars require an amplifier but can be easier on the fingers.
9. Are online resources helpful for learning guitar chords?
Yes, guitarplayers.net and other websites offer lessons, chord diagrams, and tutorials.
10. How do I stay motivated while learning guitar chords?
Set realistic goals, learn songs you love, find a practice partner, and explore different genres.
Ready to start your guitar journey? Visit guitarplayers.net to discover a wealth of resources, from beginner lessons to advanced techniques. Join our community forum to connect with fellow guitar enthusiasts, ask questions, and share your progress. Don’t wait – unlock your musical potential today with guitarplayers.net! Our address is 1140 Boylston Street, Boston, MA 02215, United States. Phone: +1 (617) 747-2261.
